Nonstructural Protein 1 of Variant PEDV Plays a Key Role in Escaping Replication Restriction by Complement C3
- PMID: 36037478
- PMCID: PMC9517699
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01024-22
Nonstructural Protein 1 of Variant PEDV Plays a Key Role in Escaping Replication Restriction by Complement C3
Abstract
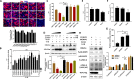
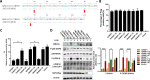
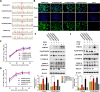
Zoonotic coronaviruses represent an ongoing threat to public health. The classical porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) first appeared in the early 1970s. Since 2010, outbreaks of highly virulent PEDV variants have caused great economic losses to the swine industry worldwide. However, the strategies by which PEDV variants escape host immune responses are not fully understood. Complement component 3 (C3) is considered a central component of the three complement activation pathways and plays a crucial role in preventing viral infection. In this study, we found that C3 significantly inhibited PEDV replication in vitro, and both variant and classical PEDV strains induced high levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in Huh7 cells. However, the PEDV variant strain reduces C3 transcript and protein levels induced by IL-1β compared with the PEDV classical strain. Examination of key molecules of the C3 transcriptional signaling pathway revealed that variant PEDV reduced C3 by inhibiting CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBP-β) phosphorylation. Mechanistically, PEDV nonstructural protein 1 (NSP1) inhibited C/EBP-β phosphorylation via amino acid residue 50. Finally, we constructed recombinant PEDVs to verify the critical role of amino acid 50 of NSP1 in the regulation of C3 expression. In summary, we identified a novel antiviral role of C3 in inhibiting PEDV replication and the viral immune evasion strategies of PEDV variants. Our study reveals new information on PEDV-host interactions and furthers our understanding of the pathogenic mechanism of this virus. IMPORTANCE The complement system acts as a vital link between the innate and the adaptive immunity and has the ability to recognize and neutralize various pathogens. Activation of the complement system acts as a double-edged sword, as appropriate levels of activation protect against pathogenic infections, but excessive responses can provoke a dramatic inflammatory response and cause tissue damage, leading to pathological processes, which often appear in COVID-19 patients. However, how PEDV, as the most severe coronavirus causing diarrhea in piglets, regulates the complement system has not been previously reported. In this study, for the first time, we identified a novel mechanism of a PEDV variant in the suppression of C3 expression, showing that different coronaviruses and even different subtype strains differ in regulation of C3 expression. In addition, this study provides a deeper understanding of the mechanism of the PEDV variant in immune escape and enhanced virulence.
Keywords: C/EBP-β; NSP1; PEDV; complement C3; replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
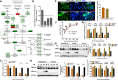
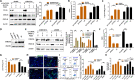
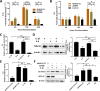
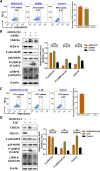
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

