Posttranslational control of lipogenesis in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 36038892
- PMCID: PMC9422141
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-022-01340-1
Posttranslational control of lipogenesis in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
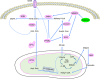
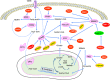
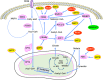
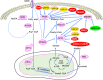
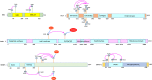
Metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells within the tumor microenvironment typically occurs in response to increased nutritional, translation and proliferative demands. Altered lipid metabolism is a marker of tumor progression that is frequently observed in aggressive tumors with poor prognosis. Underlying these abnormal metabolic behaviors are posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of lipid metabolism-related enzymes and other factors that can impact their activity and/or subcellular localization. This review focuses on the roles of these PTMs and specifically on how they permit the re-wiring of cancer lipid metabolism, particularly within the context of the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: Cancer; Lipid metabolism reprogramming; Posttranslational modification; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

