Multiple genome alignment in the telomere-to-telomere assembly era
- PMID: 36038949
- PMCID: PMC9421119
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-022-02735-6
Multiple genome alignment in the telomere-to-telomere assembly era
Abstract
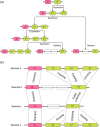
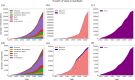
With the arrival of telomere-to-telomere (T2T) assemblies of the human genome comes the computational challenge of efficiently and accurately constructing multiple genome alignments at an unprecedented scale. By identifying nucleotides across genomes which share a common ancestor, multiple genome alignments commonly serve as the bedrock for comparative genomics studies. In this review, we provide an overview of the algorithmic template that most multiple genome alignment methods follow. We also discuss prospective areas of improvement of multiple genome alignment for keeping up with continuously arriving high-quality T2T assembled genomes and for unlocking clinically-relevant insights.
Keywords: Comparative genomics; Homology; Multiple genome alignment; Synteny.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hannenhalli S, Pevzner PA. Proceedings of IEEE 36th Annual Foundations of Computer Science. New York: IEEE; 1995. Transforming men into mice (polynomial algorithm for genomic distance problem)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

