Long-term remission under Disitamab Vedotin (RC48) in HR-positive/HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer with brain meningeal, and bone marrow involvement: A case report
- PMID: 36039062
- PMCID: PMC9404700
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13459
Long-term remission under Disitamab Vedotin (RC48) in HR-positive/HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer with brain meningeal, and bone marrow involvement: A case report
Abstract
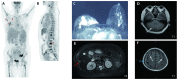
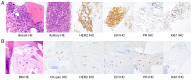
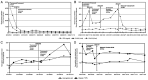
Breast cancer (BC) with overexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is closely associated with an elevated risk of multiple distant metastases and unfavorable prognosis. Disitamab Vedotin (RC48) is a newly developed antibody-drug conjugate targeting HER2, which is comprised of hertuzumab coupled to monomethyl auristatin E via a cleavable linker. Pre-clinical studies indicated its strong anti-tumor activity in HER2-positive and low HER2 expression models of BC. The present study reported on the case of a 60-year-old postmenopausal female who suffered from fatigue and was diagnosed with a right-sided BC tumor. The diagnosis was stage IV (cT4N3M1) hormone receptor (HR)-positive and HER2-positive invasive ductal carcinoma with systemic metastases (brain included). The patient initially responded well to 26 cycles of the first-line anti-HER2 targeted therapy plus chemotherapy (trastuzumab+pertuzumab+nab-paclitaxel) combined with whole-brain radiotherapy. However, both extracranial and intracranial lesions achieved progressive disease (PD), which eventually occurred during 5 sequential cycles of maintenance therapy. Subsequently, 4 cycles of second-line treatment (trastuzumab + pyrotinib + capecitabin) were continued until the levels of blood tumor markers CEA, CA15-3 and CA125 were elevated, and systemic PD was able to be attained (the brain metastases were rated as stable disease). Finally, the patient received RC48 as the third-line therapy and achieved a durable and effective clinical response. To date, the patient has benefited from 12 cycles of RC48 without any severe adverse effects. The overall survival was >3 years. The present study showcased that RC48 was effective and tolerable for a patient with HR- and HER2-positive BMBC.
Keywords: ADC; HER2-positive breast cancer; RC48; anti-HER2 target therapy; metastatic breast cancer.
Copyright: © Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
