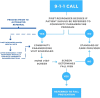
Automated referral to community paramedicine during 9-1-1 fall calls for resource activation
- PMID: 36039856
- PMCID: PMC9771950
- DOI: 10.1111/jgs.18011
Automated referral to community paramedicine during 9-1-1 fall calls for resource activation
Abstract
Background: We sought to improve the referral process to a community paramedicine (CP) program following a 9-1-1 encounter.
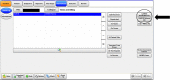
Methods: An electronic health record (EHR) for CP records with the ability to link to emergency EHR was identified and implemented with a single-click referral to the CP program. Referrals were tracked for 15 months before and after implementation.
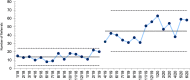
Results: Referral capacity increased from an average of 14.2 referrals per month to 44.9 referrals per month.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest an EHR is a useful investment for CP programs and may be integral to efficient program operations.
Keywords: 9-1-1; electronic health record; paramedicine; referrals.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Geriatrics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Keep on Your Feet ‐ Preventing Older Adult Falls. 2020. Accessed October 06, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/features/older-adult-falls/index.html.
-
- Stevens JA, Burns E. A CDC Compendium of Effective Fall Interventions: What Works for Community‐Dwelling Older Adults. 2015.
-
- Tinetti ME, Baker DI, McAvay G, et al. A multifactorial intervention to reduce the risk of falling among elderly people living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(13):821‐827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous