Depicting the proton relay network in human aromatase: New insights into the role of the alcohol-acid pair
- PMID: 36040260
- PMCID: PMC9366932
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4389
Depicting the proton relay network in human aromatase: New insights into the role of the alcohol-acid pair
Abstract
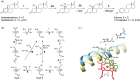
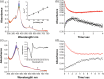
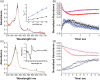
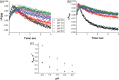
Human aromatase is the cytochrome P450 catalyzing the conversion of androgens into estrogens in a three steps reaction essential to maintain steroid hormones balance. Here we report the capture and spectroscopic characterization of its compound I (Cpd I), the main reactive species in cytochromes P450. The typical spectroscopic transitions indicating the formation of Cpd I are detected within 0.8 s when mixing aromatase with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid. The estrogen product is obtained from the same reaction mixture, demonstrating the involvement of Cpd I in aromatization reaction. Site-directed mutagenesis is applied to the acid-alcohol pair D309 and T310 and to R192, predicted to be part of the proton relay network. Mutants D309N and R192Q do not lead to Cpd I with an associated loss of activity, confirming that these residues are involved in proton delivery for Cpd I generation. Cpd I is captured for T310A mutant and shows 2.9- and 4.4-fold faster rates of formation and decay, respectively, compared to wild-type (WT). However, its activity is lower than the WT and a larger amount of H2 O2 is produced during catalysis, indicating that T310 has an essential role in proton gating for generation of Cpd 0 and Cpd I and for their stabilization. The data provide new evidences on the role of threonine belonging to the conserved "acid-alcohol" pair and known to be crucial for oxygen activation in cytochromes P450.
Keywords: alcohol-acid pair; aromatase; compound I; cytochromes P450; proton delivery.
© 2022 The Authors. Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guengerich FP. Common and uncommon cytochrome P450 reactions related to metabolism and chemical toxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2001;14:611–650. - PubMed
-
- de Montellano PRO. Cytochrome P450: Structure, mechanism, and biochemistry. 3rd ed. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2005.
-
- Denisov IG, Makris TM, Sligar SG, Schlichting I. Structure and chemistry of cytochrome P450. Chem Rev. 2005;105:2253–2277. - PubMed
-
- Guengerich FP. Human cytochrome P450 enzymes. In: Ortiz de Montellano PR, editor. Cytochrome P450: Structure, mechanism, and biochemistry. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2015; p. 523–785.
-
- Di Nardo G, Gilardi G. Natural compounds as pharmaceuticals: The key role of cytochromes P450 reactivity. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020;45:511–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

