The gateway to guanine nucleotides: Allosteric regulation of IMP dehydrogenases
- PMID: 36040265
- PMCID: PMC9375230
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4399
The gateway to guanine nucleotides: Allosteric regulation of IMP dehydrogenases
Abstract
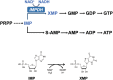
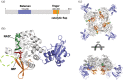
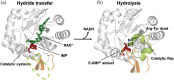
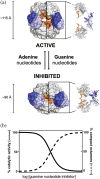
Inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that mediates the first committed step in de novo guanine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway. It is an essential enzyme in purine nucleotide biosynthesis that modulates the metabolic flux at the branch point between adenine and guanine nucleotides. IMPDH plays key roles in cell homeostasis, proliferation, and the immune response, and is the cellular target of several drugs that are widely used for antiviral and immunosuppressive chemotherapy. IMPDH enzyme is tightly regulated at multiple levels, from transcriptional control to allosteric modulation, enzyme filamentation, and posttranslational modifications. Herein, we review recent developments in our understanding of the mechanisms of IMPDH regulation, including all layers of allosteric control that fine-tune the enzyme activity.
Keywords: IMP dehydrogenase; allosteric regulation; enzyme filamentation; protein structure and function; purine nucleotide biosynthesis.
© 2022 The Authors. Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures




References
-
- Allison AC, Eugui EM. Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology. 2000;47:85–118. - PubMed
-
- Jayaram H, Cooney DA, Grusch M, Krupitza G. Consequences of IMP dehydrogenase inhibition, and its relationship to cancer and apoptosis. Curr Med Chem. 1999;6:561–574. - PubMed
-
- Braun‐Sand SB, Peetz M. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase as a target for antiviral, anticancer, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive therapeutics. Future Med Chem. 2009;2:81–92. - PubMed
-
- Cuny GD, Suebsuwong C, Ray SS. Inosine‐5′‐monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) inhibitors: A patent and scientific literature review (2002‐2016). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017;27:677–690. - PubMed
-
- Nagano N, Orengo CA, Thornton JM. One fold with many functions: The evolutionary relationships between TIM barrel families based on their sequences, structures and functions. J Mol Biol. 2002;321:741–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

