AGO104 is a RdDM effector of paramutation at the maize b1 locus
- PMID: 36040902
- PMCID: PMC9426929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273695
AGO104 is a RdDM effector of paramutation at the maize b1 locus
Abstract
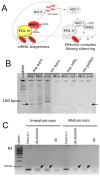
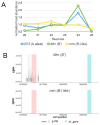
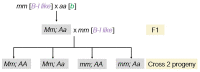
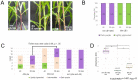
Although paramutation has been well-studied at a few hallmark loci involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in maize, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the phenomenon remain largely unknown. Previously described actors of paramutation encode components of the RNA-directed DNA-methylation (RdDM) pathway that participate in the biogenesis of 24-nucleotide small interfering RNAs (24-nt siRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs. In this study, we uncover an ARGONAUTE (AGO) protein as an effector of the RdDM pathway that is in charge of guiding 24-nt siRNAs to their DNA target to create de novo DNA methylation. We combined immunoprecipitation, small RNA sequencing and reverse genetics to, first, validate AGO104 as a member of the RdDM effector complex and, then, investigate its role in paramutation. We found that AGO104 binds 24-nt siRNAs involved in RdDM, including those required for paramutation at the b1 locus. We also show that the ago104-5 mutation causes a partial reversion of the paramutation phenotype at the b1 locus, revealed by intermediate pigmentation levels in stem tissues. Therefore, our results place AGO104 as a new member of the RdDM effector complex that plays a role in paramutation at the b1 locus in maize.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

