The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on invasive fungal infections in Africa: What have we learned?
- PMID: 36040906
- PMCID: PMC9426908
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010720
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on invasive fungal infections in Africa: What have we learned?
Abstract
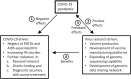
Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) have been described as diseases of the poor. The mortality rate of the infections is comparable to that of malaria, HIV, and TB, yet the infections remain poorly funded, neglected in research, and policy at all levels of human resources. The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has further worsened the current state of management for IFIs. At the same time, response to COVID-19 has stirred and boosted vaccine production, vaccine substance manufacturing, and building of next-generation sequencing capacity and genomics data sharing network in the continent. Through collaboration and transdisciplinary research effort, these network and technology can be extended to encourage fungal research to address health issues of existing and emerging fungal pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation. World Health Organisation Report of the global health observatory. 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/publications/world-health-statistics [cited Dec 2021]
-
- Africa Centre for Disease Control. Africa CDC COVID-19 Dashboard. 2022. Available from: https://africacdc.org/covid-19/ [cited 2022 Apr 16].
-
- Irwin A. How COVID spurred Africa to plot a vaccines revolution. 2021. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01048-1 [cited 2022 Jan 15]. - PubMed
-
- Global Alliance for Vaccine and Immunisation. COVID-19 impact ‘vastly underestimated’ in African countries. Zambian data challenges the assumption African populations may have been spared from COVID-19. 2021. Available from: https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/covid-19-impact-vastly-underestimated-... [cited 2022 Apr 16].
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

