Sterols in asthma
- PMID: 36041950
- PMCID: PMC9513744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2022.08.003
Sterols in asthma
Abstract
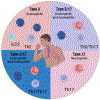
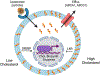
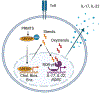
While sterols regulate immune processes key to the pathogenesis of asthma, inhibition of sterols with statin drugs has shown conflicting results in human asthma. Here, a novel understanding of the impact of sterols on type 17 immune responses and asthma lead us to hypothesize that sterols and statins may be relevant to severe asthma endotypes with neutrophil infiltration.
Keywords: Th17; asthma; neutrophilic; severe; statin; sterol.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have no interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sterols and immune mechanisms in asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Jan;151(1):47-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.09.025. Epub 2022 Oct 29. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37138729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of statins on noncholesterol sterol levels: implications for use of plant stanols and sterols.Am J Cardiol. 2005 Jul 4;96(1A):40D-46D. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.03.019. Am J Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 15992515 Review.
-
The effects of statins on the mevalonic acid pathway in recombinant yeast strains expressing human HMG-CoA reductase.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Aug 30;13:68. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-68. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24128347 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Studies of Statins in Asthma and COPD.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017;10(1):60-71. doi: 10.2174/1874467209666160112125911. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 26758945 Review.
-
[Statins and asthma].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2011 Mar 25;65:177-89. doi: 10.5604/17322693.936092. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2011. PMID: 21502694 Polish.
Cited by
-
Employing a synergistic bioinformatics and machine learning framework to elucidate biomarkers associating asthma with pyrimidine metabolism genes.Respir Res. 2024 Aug 31;25(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02954-4. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39217320 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberroside F improves airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in asthmatic mice.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023 Dec;39(12):1213-1221. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12764. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37819590 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberroside A ameliorates murine allergic airway inflammation by suppressing Th2 response and oxidative stress.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 18. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01895-8. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40825901
References
-
- Global Asthma Network The Global Asthma Report 2018, http://globalasthmareport.org/burden/burden.php
-
- Nair P. et al. (2017) Oral Glucocorticoid–Sparing Effect of Benralizumab in Severe Asthma. New England Journal of Medicine 376, 2448–2458 - PubMed

