AIMP1 promotes multiple myeloma malignancy through interacting with ANP32A to mediate histone H3 acetylation
- PMID: 36042007
- PMCID: PMC9648396
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12356
AIMP1 promotes multiple myeloma malignancy through interacting with ANP32A to mediate histone H3 acetylation
Abstract
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common hematological malignancy. An overwhelming majority of patients with MM progress to serious osteolytic bone disease. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multifunctional protein 1 (AIMP1) participates in several steps during cancer development and osteoclast differentiation. This study aimed to explore its role in MM.
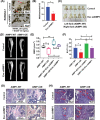
Methods: The gene expression profiling cohorts of MM were applied to determine the expression of AIMP1 and its association with MM patient prognosis. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting were used to detect AIMP1 expression. Protein chip analysis, RNA-sequencing, and chromatin immunoprecipitation and next-generation sequencing were employed to screen the interacting proteins and key downstream targets of AIMP1. The impact of AIMP1 on cellular proliferation was determined using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in vitro and a xenograft model in vivo. Bone lesions were evaluated using tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase staining in vitro. A NOD/SCID-TIBIA mouse model was used to evaluate the effect of siAIMP1-loaded exosomes on bone lesion formation in vivo.
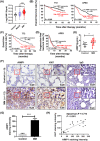
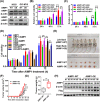
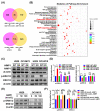
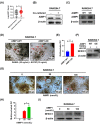
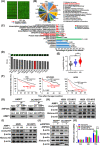
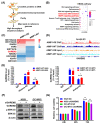
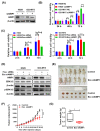
Results: AIMP1 expression was increased in MM patients and strongly associated with unfavorable outcomes. Increased AIMP1 expression promoted MM cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Protein chip assays and subsequent experiments revealed that AIMP1 interacted with acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A (ANP32A) to regulate histone H3 acetylation. In addition, AIMP1 increased histone H3 acetylation enrichment function of GRB2-associated and regulator of MAPK protein 2 (GAREM2) to increase the phosphorylation of extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2). Furthermore, AIMP1 promoted osteoclast differentiation by activating nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1) in vitro. In contrast, exosome-coated small interfering RNA of AIMP1 effectively suppressed MM progression and osteoclast differentiation in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that AIMP1 is a novel regulator of histone H3 acetylation interacting with ANP32A in MM, which accelerates MM malignancy via activation of the MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: AIMP1; ANP32A; MAPK signaling; histone H3 acetylation; multiple myeloma; osteoclast differentiation; osteolytic lesions.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ANP32A regulates histone H3 acetylation and promotes leukemogenesis.Leukemia. 2018 Jul;32(7):1587-1597. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0010-7. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Leukemia. 2018. PMID: 29467488
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase interacting multi-functional protein 1 attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGFβ signaling.Int J Oncol. 2016 Feb;48(2):747-55. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3303. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26692190
-
Assembly of the Human Multi-tRNA Synthetase Complex Through Leucine Zipper Motifs.J Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 15;436(24):168865. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168865. Epub 2024 Nov 13. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39542129
-
Stepping Out of the Cytosol: AIMp1/p43 Potentiates the Link Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity.Int Rev Immunol. 2015;34(5):367-81. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2015.1077829. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Int Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26325028 Review.
-
Roles of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multi-functional proteins in physiology and cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 24;11(7):579. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02794-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32709848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of VCP modulates NF-κB signaling pathway to suppress multiple myeloma cell proliferation and osteoclast differentiation.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Aug 21;15(16):8220-8236. doi: 10.18632/aging.204965. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37606987 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfidptosis-related immune patterns predict prognosis and characterize the tumor microenvironment in oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Feb 2;25(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05279-2. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39894803 Free PMC article.
-
The mARS complex: a critical mediator of immune regulation and homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1423510. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423510. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38975338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of VARS promotes the growth of multiple myeloma cells by causing imbalance in valine metabolism.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Jun 28;48(6):795-808. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220602. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37587064 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
AIMP1 exerts hearing protection role in age related hearing loss mice by regulating SIRT1 expression.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Aug 20;25(1):645. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06237-5. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40836274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajkumar SV, Dimopoulos MA, Palumbo A, Blade J, Merlini G, Mateos MV, et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(12):e538–48. - PubMed
-
- Rome S, Noonan K, Bertolotti P, Tariman JD, Miceli T. Bone Health, Pain, and Mobility: Evidence‐Based Recommendations for Patients With Multiple Myeloma. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2017;21(5 Suppl):47–59. - PubMed
-
- Westhrin M, Kovcic V, Zhang Z, Moen SH, Nedal TMV, Bondt A, et al. Monoclonal immunoglobulins promote bone loss in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2020;136(23):2656–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

