Intimate partner violence and its association with skilled birth attendance among women in Nigeria: evidence from the Nigeria Demographic and Health Surveys
- PMID: 36042396
- PMCID: PMC9425983
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-022-04989-1
Intimate partner violence and its association with skilled birth attendance among women in Nigeria: evidence from the Nigeria Demographic and Health Surveys
Abstract
Background: Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) has been identified as a violation of human rights and a major public health challenge. IPV against women has negative effects on women's mental well-being and leads to unfavourable health outcomes through poor maternal healthcare services utilisation, especially skilled birth attendance (SBA). This study examined the trends in IPV and SBA, as well as the different forms of IPV as predictors of SBA in Nigeria.
Methods: Data for the study were derived from a nationally representative weighted sample of 34,294 women selected and interviewed for the questions on the domestic violence module in the three consecutive Nigeria Demographic and Health Surveys conducted in 2008, 2013 and 2018. Descriptive and analytical analyses were carried out, including frequency distribution and binary logistic regression model at the multivariate level. The results of the explanatory variables were expressed as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
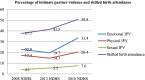
Results: The prevalence of emotional and physical IPV among the sampled women decreased in 2013 from 2008 but later increased in 2018. Sexual IPV increased from 4.1% in 2008 to 7.6% in 2018, while births delivered with the assistance of skilled providers increased from 37.7% in 2008 to 50.8% in 2018. The likelihood of using SBA significantly decreased among women who experienced emotional IPV in 2008 (aOR: 0.74; CI: 0.63-0.87) and sexual IPV in 2018 (aOR: 0.62; CI: 0.45-0.86). Women who experienced physical IPV were more likely to use SBA in 2008, 2013 and 2018 (aOR: 1.72; CI: 1.55-1.92; aOR: 1.40; CI: 1.26-1.56 and aOR: 1.33; CI: 1.15-1.54, respectively). The covariates have varying degrees of influence on SBA across the survey years.
Conclusions: The showed that the prevalence of emotional and physical IPV increased in 2018 after a decrease in 2013, with an increase in sexual IPV and the use of SBA across the survey years. Also, emotional and sexual IPV, unlike physical IPV are associated with low chances of using SBA. There is a need for more pragmatic intervention programmes towards eliminating all forms of violence against all women, reducing maternal and child mortality and promoting the empowerment of women.
Keywords: Childbearing women; Intimate partner violence; Nigeria; Skilled birth attendance; Trends.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does exposure to interparental violence increase women's risk of intimate partner violence? Evidence from Nigeria demographic and health survey.BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2018 Jan 11;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12914-018-0143-9. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2018. PMID: 29325549 Free PMC article.
-
Intimate partner violence as a factor in contraceptive discontinuation among sexually active married women in Nigeria.BMC Womens Health. 2020 Jun 17;20(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-00990-y. BMC Womens Health. 2020. PMID: 32552670 Free PMC article.
-
Empowerment, intimate partner violence and skilled birth attendance among women in rural Uganda.Reprod Health. 2016 May 4;13(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12978-016-0167-3. Reprod Health. 2016. PMID: 27141984 Free PMC article.
-
Intimate partner violence among pregnant women in Kenya: forms, perpetrators and associations.BMC Womens Health. 2022 Jun 7;22(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12905-022-01761-7. BMC Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35672817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intimate Partner Violence in Khaliji Women: A Review of the Frequency and Related Factors.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jun 28;20(13):6241. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20136241. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37444089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lethal intimate partner violence and gendered dimensions of the COVID-19 lockdown in Nigeria: evidence from a descriptive analysis of secondary data.BMJ Public Health. 2024 Mar 14;2(1):e000633. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2023-000633. eCollection 2024 Jun. BMJ Public Health. 2024. PMID: 40018252 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of intimate partner violence and male involvement on maternal healthcare services utilisation in Nigeria.Front Glob Womens Health. 2024 Mar 15;5:1353117. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2024.1353117. eCollection 2024. Front Glob Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38559815 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial variation of skilled birth attendance and associated factors among reproductive age women in Ethiopia, 2019; a spatial and multilevel analysis.Front Glob Womens Health. 2024 Aug 12;5:1082670. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2024.1082670. eCollection 2024. Front Glob Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39188539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geetika S, Mohan L, Tejbir S, Shyam DS. To study the utilization of antenatal care services among pregnant women of rural Amritsar: An interventional study. Int J Curr Res. 2015;7(5):15789–15792.
-
- United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN IGME). Levels & Trends in Child Mortality: Estimates developed by the UN IGWE, United Nations Children’s Fund, New York. Report. 2020. URL: https://www.unicef.org/media/79371/file/UN-IGME-child-mortality-report-2....
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Definition of skilled health personnel providing care during childbirth. The 2018 joint statement by WHO, the United Nations Population Fund, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Confederation of Midwives, the International Council of Nurses, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics. CH-1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/272818/WHO-RHR-18.14-en....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical