High dose insulin therapy for inotropic support during veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation decannulation: A case report
- PMID: 36042600
- PMCID: PMC9410628
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030267
High dose insulin therapy for inotropic support during veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation decannulation: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: High-dose insulin (HDI) therapy has been used as inotropic support for toxin-induced cardiogenic shock, but literature suggests that it can also be used in non-toxin-induced cardiogenic shock states. Its use has not been reported in veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) decannulation.
Patient concerns: A 56-year-old male presented with progressive dyspnea and lower extremity edema without any reported toxic ingestion.
Diagnosis: After left heart catheterization, he was diagnosed with acute biventricular nonischemic cardiac failure that ultimately required VA-ECMO support for 8 days, after which decannulation was planned.
Interventions: During decannulation, he was initiated on HDI therapy via a 1 U/kg regular insulin bolus with 25 g of dextrose and a 1 U/kg/hr insulin infusion.
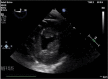
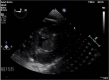
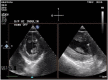
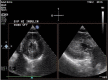
Outcomes: During the decannulation, he was monitored with transesophageal echocardiography. Initially, left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) was estimated at 10% to 15%. Transesophageal echocardiography after HDI but prior to decannulation showed LVEF 30% to 40%. Transthoracic echocardiography 3.5 hours after HDI bolus and decannulation revealed normal LV systolic function; LVEF 50% to 55%.
Lessons: While multiple interventions occurred during decannulation, HDI therapy may have assisted in transitioning off ECMO support, and HDI should be investigated as an adjunctive option in future decannulations and other non-toxin-induced cardiogenic shock states.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Engebretsen KM, Kaczmarek KM, Morgan J, et al. . High-dose insulin therapy in beta-blocker and calcium channel-blocker poisoning. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011;49:277–83. - PubMed
-
- Koskenkari JK, Kaukoranta PK, Kiviluoma KT, et al. . Metabolic and hemodynamic effects of high-dose insulin treatment in aortic valve and coronary surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80:511–7. - PubMed
-
- Hiesmayr M, Haider WJ, Grubhofer G, et al. . Effects of dobutamine versus insulin on cardiac performance, myocardial oxygen demand, and total body metabolism after coronary artery bypass grafting. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1995;9:653–8. - PubMed
-
- Taylor SH, Majid PA. Insulin and the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1971;2:293–317. - PubMed
-
- Kline JA, Leonova E, Raymond RM. Beneficial myocardial metabolic effects of insulin during verapamil toxicity in the anesthetized canine. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:1251–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

