Genetic polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36042908
- PMCID: PMC9375530
- DOI: 10.5937/jomb0-34155
Genetic polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To systematically analyze the influence of genetic polymorphisms of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) on susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods: Relevant literatures reporting MMP9 and susceptibility to COPD in PubMed, Web of Science, VIP, Wanfang and CNKI databases were searched using the key words "matrix metalloproteinases 9/MMP9, COPD/chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Data of eligible literatures were extracted and analyzed for the odds ratio (OR) and corresponding 95% CI.
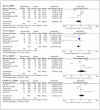
Results: A total of 16 independent studies reporting MMP9-1562C/T and COPD patients were enrolled and analyzed. None of the genetic models revealed the relationship between MMP9-1562C/T and susceptibility to COPD. Subgroup analyses identified lower risk of COPD in Chinese population carrying the TT genotype for theMMP9 rs3918242 relative to those carrying CT and CC genotypes (P=0.03, OR=0.67, 95% CI=0.46-0.97).
Conclusions: Chinese population carrying the TT genotype for the MMP-9 rs3918242 present lower susceptibility to COPD relative to those carrying CT and CC genotypes.
Uvod: Sistematska analiza uticaja genetskih polimorfizama matriks metaloproteinaze 9 (MMP9) na osetljivost hronične opstruktivne bolesti pluća (HOBP).
Metode: Relevantna literatura koja izveštava o MMP9 i podložnosti HOBP u bazama podataka PubMed, Web of Scince, VIP, Wanfang i CNKI pretraživana je korišćenjem ključnih reči "matriks metaloproteinaze 9/MMP9, COPD/hronična opstruktivna bolest pluća". Podaci iz kvalifikovane literature su ekstrahovani i analizirani za odnos šanse (OR) i odgovarajući 95% CI.
Rezultati: Ukupno je uključeno i analizirano 16 nezavisnih studija koje su izveštavale o pacijentima sa MMP9-1562C/T i HOBP. Nijedan od genetskih modela nije otkrio vezu između MMP9-1562C/T i osetljivosti na HOBP. Analize podgrupa identifikovale su niži rizik od HOBP kod kineske populacije koja nosi TT genotip za MMP-9 rs3918242 u odnosu na one koji nose CT i CC genotipove (P=0,03, OR=0,67, 95% CI=0,46-0,97).
Zaključak: Kineska populacija koja nosi TT genotip za MMP9 rs3918242 predstavlja manju osetljivost na HOBP u odnosu na one sa CT i CC genotipovima.
Keywords: COPD; MMP9; meta-analysis; polymorphism.
2022 Xiaoping Yang, Yuanyuan Yu, Yong Wang, Wen Jiang, Wenqing Jiang, Bin Yin, published by CEON/CEES.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors stated that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures







References
-
- Clancy J, Nobes M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Nature-nurture interactions. Br J Nurs. 2012;21(13):772. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
