Clinical and neurocognitive outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) with cerebral protection: initial experience with a novel dual-filter device in Southeast Asia
- PMID: 36043277
- PMCID: PMC9297182
- DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2022030
Clinical and neurocognitive outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) with cerebral protection: initial experience with a novel dual-filter device in Southeast Asia
Abstract
Introduction: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is increasingly performed in patients with severe aortic stenosis. A novel dual-filter system to reduce cerebral embolism during TAVI recently became available. We aimed to assess the feasibility, safety, and clinical and neurocognitive outcomes of TAVI with cerebral protection in Asian patients.
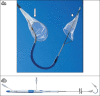
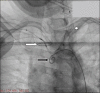
Methods: 40 consecutive patients undergoing TAVI with cerebral protection were enrolled. All procedures were performed via femoral access using the self-expanding Evolut R/PRO or Portico, or the balloon-expandable SAPIEN 3 bioprostheses. Baseline characteristics, procedural and clinical outcomes were recorded. Cognition was assessed at baseline and 30 days using the abbreviated mental test (AMT).
Results: The mean age of the patients (75% male) was 76.4 ± 8.4 years. TAVI was uncomplicated in all patients. The filter device was successfully deployed in 38 (95.0%) patients without safety issues. There was no stroke or death at 30 days, and the survival rate at nine months was 95.0%. There was no overall cognitive change (baseline vs. 30-day AMT: 9.2 ± 1.1 vs. 9.0 ± 1.5, p = 0.12), and only 1 (2.5%) patient developed impaired cognition at 30 days. Patients with a decreased AMT score at 30 days were significantly older than those without (82.1 ± 4.5 vs. 74.4 ± 7.7 years, p = 0.019). All patients with decreased AMT scores were aged ≥ 76 years.
Conclusion: In this early Asian experience of TAVI under cerebral protection, the filter device was successfully deployed in 95% of patients, with 100% procedural success. There were no filter-related complications and no stroke or mortality at 30 days. Overall cognition was preserved, although increased age was associated with a decline in AMT score.
Keywords: Asia; aortic valve stenosis; cognition; stroke; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
Copyright: © Singapore Medical Association.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of a Cerebral Protection Device on Brain Lesions Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis: The CLEAN-TAVI Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2016 Aug 9;316(6):592-601. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.10302. JAMA. 2016. PMID: 27532914 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimalistic Approach for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI): Open Vascular Vs. Fully Percutaneous Approach.Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2019 Oct 1;40(2):5-14. doi: 10.2478/prilozi-2019-0009. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2019. PMID: 31605589
-
Percutaneous transcatheter aortic valve implantation for degenerated surgical bioprostheses: the first case series in Asia with one-year follow-up.Singapore Med J. 2016 Jul;57(7):401-5. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016097. Epub 2016 May 19. Singapore Med J. 2016. PMID: 27193081 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of short- and long-term clinical outcomes of the self-expanding Evolut R/pro valve versus the balloon-expandable Sapien 3 valve for transcatheter aortic valve implantation.Int J Cardiol. 2023 Jan 15;371:100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.09.035. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Int J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36130623
-
Updated clinical indications for transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with severe aortic stenosis: expert opinion of the Italian Society of Cardiology and GISE.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2018 May;19(5):197-210. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000636. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2018. PMID: 29578921 Review.
References
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1597–607. - PubMed
-
- Smith CR, Leon MB, Mack MJ, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2187–98. - PubMed
-
- Adams DH, Popma JJ, Reardon MJ, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a self-expanding prosthesis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1790–8. - PubMed
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack MJ, et al. Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1609–20. - PubMed
-
- Reardon MJ, Van Mieghem NM, Popma JJ, et al. Surgical or transcatheter aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1321–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

