Ketogenic Diet: An Effective Treatment Approach for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 36043794
- PMCID: PMC9890290
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X20666220830102628
Ketogenic Diet: An Effective Treatment Approach for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
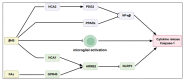
This review discusses the effects and mechanisms of a ketogenic diet on neurodegenerative diseases on the basis of available evidence. A ketogenic diet refers to a high-fat, mediumprotein, and low-carbohydrate diet that leads to a metabolic shift to ketosis. This review systematically summarizes the scientific literature supporting this effective treatment approach for neurodegenerative diseases, including effects on mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, neuroinflammation, and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. It also highlights the clinical evidence for the effects of the ketogenic diet in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and motor neuron disease. Finally, it discusses the common adverse effects of ketogenic therapy. Although the complete mechanism of the ketogenic diet in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases remains to be elucidated, its clinical efficacy has attracted many new followers. The ketogenic diet is a good candidate for adjuvant therapy, but its specific applicability depends on the type and the degree of the disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Ketogenic diet; Parkinson's disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; brain gut axis.; neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
References
-
- Cunnane S.C., Courchesne-Loyer A., St-Pierre V., Vandenberghe C., Pierotti T., Fortier M., Croteau E., Castellano C.A. Can ketones compensate for deteriorating brain glucose uptake during aging? Implications for the risk and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016;1367(1):12–20. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12999. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical