Real-world effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments in Germany
- PMID: 36044096
- PMCID: PMC9512727
- DOI: 10.1007/s11657-022-01156-z
Real-world effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments in Germany
Erratum in
-
Correction: Real-world effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments in Germany.Arch Osteoporos. 2022 Sep 27;17(1):129. doi: 10.1007/s11657-022-01167-w. Arch Osteoporos. 2022. PMID: 36163557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
This observational study assessed the impact on the fracture incidence of osteoporosis medications in postmenopausal women in Germany. Continued treatment with osteoporosis medications was associated with reductions of fracture rates in a real-world setting.
Purpose: The efficacy of osteoporosis medications has been demonstrated in clinical trials, but a lack of evidence exists of their real-world effectiveness. This real-world study assessed the treatment patterns and impact on the fracture incidence of osteoporosis medications in postmenopausal women in Germany.
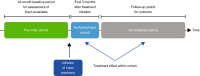
Methods: This cohort study used data from the WIG2 benchmark database, a German anonymised healthcare claims database. All women ≥ 50 years of age with ≥ 1 prescription for osteoporosis medication between 1 January 2013 and 31 December 2017 were included. The primary outcome was treatment effectiveness, evaluated as the change in fracture incidence after initiating treatment. Fracture types included all fractures, clinical vertebral, hip and wrist/forearm. Fracture incidence was assessed during the early-treatment period (0-3 months) and the on-treatment period (4-12, 13-24, 25-36 and 37-48 months).
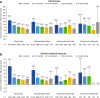
Results: Baseline covariates and treatment patterns were determined for 41,861 patients. The median duration of therapy was longer with denosumab (587 days) than with intravenous ibandronate (451 days), intravenous zoledronate (389 days) or oral bisphosphonates (258 days). The baseline incidence rate of all fractures was higher in patients receiving denosumab than in those receiving other treatments (87.6, 78.2, 56.6 and 66.0 per 1000 person-years for denosumab, oral bisphosphonates, intravenous ibandronate and intravenous zoledronate, respectively). Rates of all fractures declined with continued denosumab (by 38%, 50%, 56% and 67% at 12, 24, 36 and 48 months, respectively) and oral bisphosphonates (by 39%, 44%, 49% and 42%, respectively) treatment.
Conclusion: Continued treatment with osteoporosis medications was associated with reductions of fracture rates in a real-world setting.
Keywords: Fracture rate; Germany; Postmenopausal osteoporosis; Real-world; Retrospective cohort.
© 2022. International Osteoporosis Foundation and Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
JOK is an employee of Amgen Ltd; RB is an employee of Amgen GmbH. NK and JB are employees of WIG2 GmbH, funded by Amgen. MP is an employee of Kantar GmbH, funded by Amgen. PH has received grants/research, consultancy and lecture fees from Amgen, Besins, Elli Lilly, Exeltis, Gedeon Richter, Hexal, Hologic, Novartis, Pfizer, Stada and UCB.
Figures


References
-
- Khalid S, Reyes C, Ernst M, Delmestri A, Toth E, Libanati C, Abrahamsen B, Prieto-Alhambra D. One- and 2-year incidence of osteoporotic fracture: a multi-cohort observational study using routinely collected real-world data. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33:123–137. doi: 10.1007/s00198-021-06077-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergård M, Compston J, Cooper C, Stenmark J, McCloskey EV, Jönsson B, Kanis JA. Osteoporosis in the European Union: medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA) Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8:136. doi: 10.1007/s11657-013-0136-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

