Pirfenidone and post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis: invoked again for realistic goals
- PMID: 36044102
- PMCID: PMC9430017
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-022-01027-6
Pirfenidone and post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis: invoked again for realistic goals
Abstract
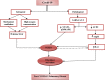
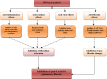
Pirfenidone (PFN) is an anti-fibrotic drug with significant anti-inflammatory property used for treatment of fibrotic conditions such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). In the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) era, severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2) could initially lead to acute lung injury (ALI) and in severe cases may cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) which is usually resolved with normal lung function. However, some cases of ALI and ARDS are progressed to the more severe critical stage of pulmonary fibrosis commonly named post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis which needs an urgent address and proper management. Therefore, the objective of the present study was to highlight the potential role of PFN in the management of post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis. The precise mechanism of post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis is related to the activation of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β1), which activates the release of extracellular proteins, fibroblast proliferation, fibroblast migration and myofibroblast conversion. PFN inhibits accumulation and recruitment of inflammatory cells, fibroblast proliferation, deposition of extracellular matrix in response to TGFβ1 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, PFN suppresses furin (TGFβ1 convertase activator) a protein effector involved in the entry of SARS-CoV-2 and activation of TGFβ1, and thus PFN reduces the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2. Besides, PFN modulates signaling pathways such as Wingless/Int (Wnt/β-catenin), Yes-Associated Protein (YAP)/Transcription Co-Activator PDZ Binding Motif (TAZ) and Hippo Signaling Pathways that are involved in the pathogenesis of post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis. In conclusion, the anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties of PFN may attenuate post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: Anti-Fibrotic; Anti-Inflammatory; Covid-19; Pirfenidone; Pulmonary Fibrosis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ali RM, Ghonimy MB. Post-COVID-19 pneumonia lung fibrosis: a worrisome sequelae in surviving patients. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 2021;52(1):1–8. doi: 10.1186/s43055-021-00484-3. - DOI
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Naimi MS, Lungnier CM, Al-Gareeb AI. Macrolides and COVID-19: an optimum premise. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. 2020;4(3):189. doi: 10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_103_20. - DOI
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Niemi MS, Hussain NR, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Harchan NA, Al-Kurashi AH. The Potential Role of Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) in COVID-19: Navigating the Uncharted. In: Kibel A, editor. Selected chapters from the reninangiotensin system. London: IntechOpen; 2020. pp. 151–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
