Amelioration of pathologic α-synuclein-induced Parkinson's disease by irisin
- PMID: 36044549
- PMCID: PMC9457183
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2204835119
Amelioration of pathologic α-synuclein-induced Parkinson's disease by irisin
Abstract
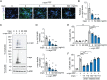
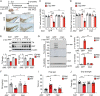
Physical activity provides clinical benefit in Parkinson's disease (PD). Irisin is an exercise-induced polypeptide secreted by skeletal muscle that crosses the blood-brain barrier and mediates certain effects of exercise. Here, we show that irisin prevents pathologic α-synuclein (α-syn)-induced neurodegeneration in the α-syn preformed fibril (PFF) mouse model of sporadic PD. Intravenous delivery of irisin via viral vectors following the stereotaxic intrastriatal injection of α-syn PFF cause a reduction in the formation of pathologic α-syn and prevented the loss of dopamine neurons and lowering of striatal dopamine. Irisin also substantially reduced the α-syn PFF-induced motor deficits as assessed behaviorally by the pole and grip strength test. Recombinant sustained irisin treatment of primary cortical neurons attenuated α-syn PFF toxicity by reducing the formation of phosphorylated serine 129 of α-syn and neuronal cell death. Tandem mass spectrometry and biochemical analysis revealed that irisin reduced pathologic α-syn by enhancing endolysosomal degradation of pathologic α-syn. Our findings highlight the potential for therapeutic disease modification of irisin in PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; irisin; neurodegeneration; synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: B.M.S. holds issued and pending patents related to irisin and the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. T.-I.K., H.K., B.M.S., and T.M.D. hold pending patents related to irisin and the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. B.M.S. is a co-founder of Aevum Therapeutics, Inc, which is developing irisin for therapeutics of neurodegeneration. C.D.W. holds a patent related to irisin (WO2015051007A1) and is an academic co-founder and consultant for Aevum Therapeutics. C.D.W. has a financial interest in Aevum Therapeutics, a company developing drugs which harness the protective molecular mechanisms of exercise to treat neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders. C.D.W.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Berardelli A., Rothwell J. C., Thompson P. D., Hallett M., Pathophysiology of bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 124, 2131–2146 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Jankovic J., Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 368–376 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Asahina M., Vichayanrat E., Low D. A., Iodice V., Mathias C. J., Autonomic dysfunction in parkinsonian disorders: Assessment and pathophysiology. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 84, 674–680 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Mehra S., Sahay S., Maji S. K., α-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation: Implications in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Proteins Proteomics 1867, 890–908 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

