A targetable pathway in neutrophils mitigates both arterial and venous thrombosis
- PMID: 36044595
- PMCID: PMC10318551
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7465
A targetable pathway in neutrophils mitigates both arterial and venous thrombosis
Abstract
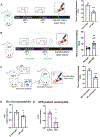
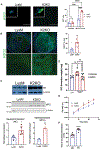
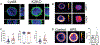
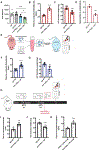
Arterial and venous thrombosis constitutes a major source of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Long considered as distinct entities, accumulating evidence indicates that arterial and venous thrombosis can occur in the same populations, suggesting that common mechanisms are likely operative. Although hyperactivation of the immune system is a common forerunner to the genesis of thrombotic events in both vascular systems, the key molecular control points remain poorly understood. Consequently, antithrombotic therapies targeting the immune system for therapeutics gain are lacking. Here, we show that neutrophils are key effectors of both arterial and venous thrombosis and can be targeted through immunoregulatory nanoparticles. Using antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) as a model for arterial and venous thrombosis, we identified the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) as a key regulator of neutrophil activation. Upon activation through genetic loss of KLF2 or administration of antiphospholipid antibodies, neutrophils clustered P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) by cortical actin remodeling, thereby increasing adhesion potential at sites of thrombosis. Targeting clustered PSGL-1 using nanoparticles attenuated neutrophil-mediated thrombosis in APS and KLF2 knockout models, illustrating the importance and feasibility of targeting activated neutrophils to prevent pathological thrombosis. Together, our results demonstrate a role for activated neutrophils in both arterial and venous thrombosis and identify key molecular events that serve as potential targets for therapeutics against diverse causes of immunothrombosis.
Figures



Comment in
-
Target neutrophils to treat thrombotic APS?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;18(12):673. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00866-5. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 36309633 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aird WC, Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium. Circ. Res 100, 174–190 (2007). - PubMed
-
- von Brühl ML, Stark K, Steinhart A, Chandraratne S, Konrad I, Lorenz M, Khandoga A, Tirniceriu A, Coletti R, Köllnberger M, Byrne RA, Laitinen I, Walch A, Brill A, Pfeiler S, Manukyan D, Braun S, Lange P, Riegger J, Ware J, Eckart A, Haidari S, Rudelius M, Schulz C, Echtler K, Brinkmann V, Schwaiger M, Preissner KT, Wagner DD, Mackman N, Engelmann B, Massberg S, Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J. Exp. Med 209, 819–835 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

