OXTRHigh stroma fibroblasts control the invasion pattern of oral squamous cell carcinoma via ERK5 signaling
- PMID: 36045118
- PMCID: PMC9433374
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32787-y
OXTRHigh stroma fibroblasts control the invasion pattern of oral squamous cell carcinoma via ERK5 signaling
Abstract
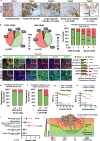
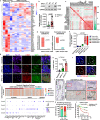
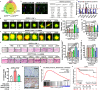
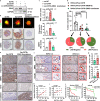
The Pattern Of Invasion (POI) of tumor cells into adjacent normal tissues clinically predicts postoperative tumor metastasis/recurrence of early oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), but the mechanisms underlying the development of these subtypes remain unclear. Focusing on the highest score of POIs (Worst POI, WPOI) present within each tumor, we observe a disease progression-driven shift of WPOI towards the high-risk type 4/5, associated with a mesenchymal phenotype in advanced OSCC. WPOI 4-5-derived cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFsWPOI4-5), characterized by high oxytocin receptor expression (OXTRHigh), contribute to local-regional metastasis. OXTRHigh CAFs induce a desmoplastic stroma and CCL26 is required for the invasive phenotype of CCR3+ tumors. Mechanistically, OXTR activates nuclear ERK5 transcription signaling via Gαq and CDC37 to maintain high levels of OXTR and CCL26. ERK5 ablation reprograms the pro-invasive phenotype of OXTRHigh CAFs. Therefore, targeting ERK5 signaling in OXTRHigh CAFs is a potential therapeutic strategy for OSCC patients with WPOI 4-5.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Impact of worst pattern of invasion on prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2023 Oct;51(10):3000605231206260. doi: 10.1177/03000605231206260. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37871621 Free PMC article.
-
Epiregulin reprograms cancer-associated fibroblasts and facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion via JAK2-STAT3 pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 24;38(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1277-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31234944 Free PMC article.
-
New Histopathologic Risk Model for Early T-stage Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Focusing on a Modified Worst Pattern of Invasion System and a New Tumor Budding Score.Am J Surg Pathol. 2024 Jan 1;48(1):59-69. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002136. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Am J Surg Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37779502
-
Biopsy pattern of invasion type to determine the surgical approach in early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma.Virchows Arch. 2021 Jul;479(1):109-119. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-03008-y. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Virchows Arch. 2021. PMID: 33438091
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Malignancy with Focus on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1300. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021300. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA expression as a prognostic biomarker of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC): a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Mar 31;24(1):406. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04182-0. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38556858 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of worst pattern of invasion on prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2023 Oct;51(10):3000605231206260. doi: 10.1177/03000605231206260. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37871621 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-killed Prevotella intermedia promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of tumor suppressors and affecting the tumor microenvironment.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Mar 21;13(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00500-y. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38515216 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Interact with Schwann Cells for Tumor Perineural Invasion by Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Neurosci Bull. 2025 Jun;41(6):1003-1020. doi: 10.1007/s12264-025-01364-w. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Neurosci Bull. 2025. PMID: 39998796
-
Multiperspective quantitative tumor-stroma ratio reveals histological areas associated with poor outcomes in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2023 Jun;12(11):12161-12172. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5909. Epub 2023 May 15. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37184217 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

