The development of dissolved oxygen forecast model using hybrid machine learning algorithm with hydro-meteorological variables
- PMID: 36045185
- PMCID: PMC9894995
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-022-22601-z
The development of dissolved oxygen forecast model using hybrid machine learning algorithm with hydro-meteorological variables
Abstract
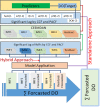
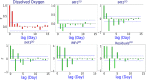
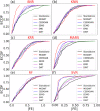
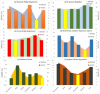
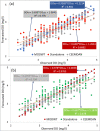
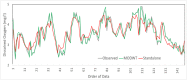
Dissolved oxygen (DO) forecasting is essential for aquatic managers responsible for maintaining ecosystem health and the management of water bodies affected by water quality parameters. This paper aims to forecast dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration using a multivariate adaptive regression spline (MARS) hybrid model coupled with maximum overlap discrete wavelet transformation (MODWT) as a feature decomposition approach for Surma River water using a set of water quality hydro-meteorological variables. The proposed hybrid model is compared with numerous machine learning methods, namely Bayesian ridge regression (BNR), k-nearest neighbourhood (KNN), kernel ridge regression (KRR), random forest (RF), and support vector regression (SVR). The investigational results show that the proposed model of MODWT-MARS has a better prediction than the comparing benchmark models and individual standalone counter parts. The result shows that the hybrid algorithms (i.e. MODWT-MARS) outperformed the other models (r = 0.981, WI = 0.990, RMAE = 2.47%, and MAE = 0.089). This hybrid method may serve to forecast water quality variables with fewer predictor variables.
Keywords: Bangladesh; Dissolved oxygen; Forecasting; Hybrid model; MARS; MODWT; Surma River.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Adamowski J, Fung Chan H, Prasher SO, Ozga-Zielinski B, Sliusarieva A (2012) Comparison of multiple linear and nonlinear regression, autoregressive integrated moving average, artificial neural network, and wavelet artificial neural network methods for urban water demand forecasting in Montreal, Canada. Water Resour Res 48(1)
-
- Agbinya JI (1996) Discrete wavelet transform techniques in speech processing, Proceedings of Digital Processing Applications (TENCON’96). IEEE 2:514–519
-
- Ahmed AAM. Prediction of dissolved oxygen in Surma River by biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand using the artificial neural networks (ANNs) J King Saud Univ Eng Sci. 2017;29(2):151–158.
-
- Ahmed MH, Lin L-S. Dissolved oxygen concentration predictions for running waters with different land use land cover using a quantile regression forest machine learning technique. J Hydrol. 2021;597:126213.
-
- Ahmed AAM, Shah SMA. Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) to estimate the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of Surma River. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci. 2017;29(3):237–243.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

