Prognostic factors and scoring systems associated with outcome in pediatric acute liver failure
- PMID: 36045327
- PMCID: PMC9429365
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-022-03574-x
Prognostic factors and scoring systems associated with outcome in pediatric acute liver failure
Abstract
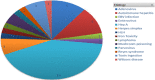
Background: Pediatric acute liver failure (PALF) is an uncommon, devastating illness with significant mortality. Liver transplantation remains the mainstay of treatment for irreversible PALF. The purpose of this study was to determine the etiology and prognostic factors associated with outcome of PALF in South Africa and to evaluate prognostic scoring systems used.
Methods: Records of 45 pediatric patients younger than 16 years of age who presented with PALF from 1 January 2015 till 31 October 2020 were analysed. Patients were divided into two groups with one group consisting of patients with spontaneous recovery of the liver with supportive treatment (6/45:13.3%) and the second group consisting of patients with poor outcomes who demised (19/45: 42%) or underwent liver transplantation (20/45: 44%).
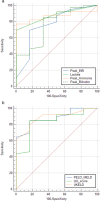
Results: The median age of presentation was 3.3 years (IQR 1.8-6.9) with the 1-5 years age group constituting majority of patients (55.6%). Median time to follow up was 6.1 months (IQR 0.2-28.8). Higher liver injury unit scores were observed in patients who had poorer outcomes (P = 0.008) with a threshold of greater than 246 having a sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 83% (P < 0.001). Higher peak PELD/MELD (P = 0.006) and admission UKELD (P = 0.002) scores, were found in patients with poorer outcomes. Kings College Hospital criteria (KCHC) was useful in predicting which patients would die without liver transplantation (P = 0.002). Liver transplantation was performed in 20/45 (44%) patients with a post transplantation 1 year patient and graft survival of 80%.
Conclusion: Although, survival of PALF patients was lower than high and other low-middle income countries, outcomes post transplantation were good. Our study demonstrates the utility of dynamic scoring systems in PALF patients, it underscores the need for early referral and clinical monitoring in a tertiary center once the criteria for PALF have been met.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Complications of liver transplantation; Hepatitis A virus; Liver injury unit score; Pediatric end-stage liver disease score; Pediatric liver transplantation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pediatric acute liver failure: etiology, outcomes, and the role of serial pediatric end-stage liver disease scores.Pediatr Transplant. 2013 Jun;17(4):362-8. doi: 10.1111/petr.12083. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Pediatr Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23586473
-
Etiology, outcome and prognostic indicators of acute liver failure in Asian children.Hepatol Int. 2022 Dec;16(6):1390-1397. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10417-5. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Hepatol Int. 2022. PMID: 36131224
-
Etiology, outcome and prognostic factors of childhood acute liver failure in a German Single Center.Ann Hepatol. 2015 Sep-Oct;14(5):722-8. Ann Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26256901
-
Prognostic modeling in pediatric acute liver failure.Liver Transpl. 2016 Oct;22(10):1418-30. doi: 10.1002/lt.24501. Liver Transpl. 2016. PMID: 27343006 Review.
-
Pediatric acute liver failure: Current perspective in etiology and management.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr;43(2):349-360. doi: 10.1007/s12664-024-01520-6. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38466551 Review.
Cited by
-
[Advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric acute liver failure].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 15;26(2):194-200. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2309015. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38436319 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
CHALF Score: A Novel Tool to Rapidly Risk Stratify Children in Need of Liver Transplant Evaluation During Acute Liver Failure.Transplantation. 2024 Apr 1;108(4):930-939. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004845. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Transplantation. 2024. PMID: 37867246 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-transplant predictors of 3-Month survival following liver transplantation for acute liver failure in adult and pediatric patients in Türkiye.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 19;15(1):26221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11298-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40683961 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of mortality from hepatitis A virus-related acute liver failure in children-Do we have the perfect prognostic model?Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr;43(2):292-295. doi: 10.1007/s12664-024-01574-6. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38630419 No abstract available.
-
Prognostic markers in hepatitis A-related pediatric acute liver failure and validation of the Peds-hepatitis A virus prognostic model.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr;43(2):459-467. doi: 10.1007/s12664-024-01551-z. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38568354
References
-
- Bansal S, Dhawan A. Acute liver failure. Curr Paediatr. 2006;16(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cupe.2005.12.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

