BAG6 negatively regulates the RLR signaling pathway by targeting VISA/MAVS
- PMID: 36045679
- PMCID: PMC9420869
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.972184
BAG6 negatively regulates the RLR signaling pathway by targeting VISA/MAVS
Abstract
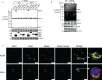
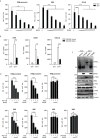
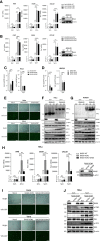
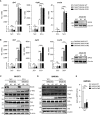
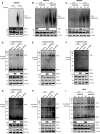
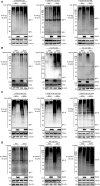
The virus-induced signaling adaptor protein VISA (also known as MAVS, ISP-1, Cardif) is a critical adaptor protein in the innate immune response to RNA virus infection. Upon viral infection, VISA self-aggregates to form a sizeable prion-like complex and recruits downstream signal components for signal transduction. Here, we discover that BAG6 (BCL2-associated athanogene 6, formerly BAT3 or Scythe) is an essential negative regulator in the RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. BAG6 inhibits the aggregation of VISA by promoting the K48-linked ubiquitination and specifically attenuates the recruitment of TRAF2 by VISA to inhibit RLR signaling. The aggregation of VISA and the interaction of VISA and TRAF2 are enhanced in BAG6-deficient cell lines after viral infection, resulting in the enhanced transcription level of downstream antiviral genes. Our research shows that BAG6 is a critical regulating factor in RIG-I/VISA-mediated innate immune response by targeting VISA.
Keywords: BAG6; TRAF2; VISA/MAVS; innate immunity; interferon.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Li, Xiao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

