Pityriasis Versicolor Resistant to Antifungal Drugs in a Patient in Lomé (Togo)
- PMID: 36045944
- PMCID: PMC9424034
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5404913
Pityriasis Versicolor Resistant to Antifungal Drugs in a Patient in Lomé (Togo)
Abstract
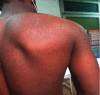
Background: Pityriasis versicolor (PV) is a ubiquitous superficial skin mycosis that often affects young adults. It is often effectively treated with local or oral antifungal agents. Cases of PV resistance to antifungal agents have been reported rarely. We report a case of antifungal resistant PV. Observation. A 22-year-old patient was followed since the age of 17 years in a dermatology outpatient clinic for hyperpigmented scaly macular lesions of the trunk and upper limbs. The clinical diagnosis of PV was retained. The patient was treated by fluconazole 300 mg/week before being lost to follow-up. He was seen again in 2019 (about 2 years later) for the same symptomatology and treated again by fluconazole and ciclopirox olamine cream without improvement. He was again lost to follow-up and seen again six months later. A mycological sample was taken and Aspergillus niger was isolated. The patient was treated by itraconazole for 6 weeks. The evolution was marked by a clinical status quo. The patient was again put on salicylated petroleum jelly 10% associated with terbinafine cream and then lost to follow-up.
Conclusion: The emergence of fungal resistance to antifungal drugs does not spare PV. It can therefore be resistant to several antifungal drugs, leaving clinicians and patients in despair.
Copyright © 2022 Julienne Teclessou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antifungal Treatment for Pityriasis Versicolor.J Fungi (Basel). 2015 Mar 12;1(1):13-29. doi: 10.3390/jof1010013. J Fungi (Basel). 2015. PMID: 29376896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral therapy of common superficial fungal infections of the skin.J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999 Jun;40(6 Pt 2):S31-4. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70395-6. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999. PMID: 10367914 Review.
-
Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of Unani Formulations in Pityriasis Versicolor: A randomized controlled trial.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115603. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115603. Epub 2022 Aug 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35940465 Clinical Trial.
-
Can pityriasis versicolor be treated with 2% ketoconazole foam?J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Jul;13(7):855-9. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25007370 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of tinea versicolor with a new antifungal agent, ciclopirox olamine cream 1%.Clin Ther. 1985;7(5):574-83. Clin Ther. 1985. PMID: 2865009 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Szepietowski J. C., Baran E., Wild E. Tinea versicolor: a prospective study. Korean journal of medical mycology . 2000;5:108–112.
-
- El Euch D., Riahi I., Mokni M., Ben Osman A., Mezlini S., Abidi H. [Ketoconazole foaming gel in tinea versicolor (report of 60 cases)] Tunisie Medicale . 1999;77(1):38–40. - PubMed
-
- Faergemann J. The role of Malassezia yeasts in skin diseases. Mikologia Lekarska . 2004;11:129–133.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources