Anoikis resistance in diffuse glioma: The potential therapeutic targets in the future
- PMID: 36046036
- PMCID: PMC9423707
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.976557
Anoikis resistance in diffuse glioma: The potential therapeutic targets in the future
Abstract
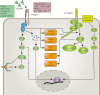
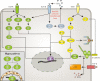
Glioma is the most common malignant intracranial tumor and exhibits diffuse metastasis and a high recurrence rate. The invasive property of glioma results from cell detachment. Anoikis is a special form of apoptosis that is activated upon cell detachment. Resistance to anoikis has proven to be a protumor factor. Therefore, it is suggested that anoikis resistance commonly occurs in glioma and promotes diffuse invasion. Several factors, such as integrin, E-cadherin, EGFR, IGFR, Trk, TGF-β, the Hippo pathway, NF-κB, eEF-2 kinase, MOB2, hypoxia, acidosis, ROS, Hsp and protective autophagy, have been shown to induce anoikis resistance in glioma. In our present review, we aim to summarize the underlying mechanism of resistance and the therapeutic potential of these molecules.
Keywords: anoikis resistance; apoptosis; glioma; molecular pathways; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Fang, Xu, Yuan, Du, Ni, Xu, Shao, Zhang and Lou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

