Pathogenic mechanisms involving the interplay between adipose tissue and auto-antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 36046189
- PMCID: PMC9421387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104893
Pathogenic mechanisms involving the interplay between adipose tissue and auto-antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
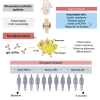
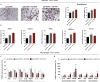
We aimed to evaluate the association between adipose tissue (AT) dysfunction, autoimmunity, and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A cross-sectional study including 150 RA patients and 50 healthy donors and longitudinal study with 122 RA patients treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, anti-interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R) or anti-CD20 therapies for 6 months were carried out. In vitro experiments with human AT and adipocyte and macrophage cell lines were performed. A collagen-induced arthritis mouse model was developed. The insulin resistance and the altered adipocytokine profile were associated with disease activity, the presence of anti-citrullinated proteins anti-bodies (ACPAs), and worse response to therapy in RA. AT in the context of arthritis is characterized by an inflammatory state alongside the infiltration of macrophages and B/plasmatic cells, where ACPAs can have a direct impact, inducing inflammation and insulin resistance in macrophages and promoting a defective adipocyte differentiation, partially restored by biologicals.
Keywords: Health sciences; Immunology; Rheumatology.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Aletaha D., Neogi T., Silman A.J., Funovits J., Felson D.T., Bingham C.O., 3rd, Birnbaum N.S., Burmester G.R., Bykerk V.P., Cohen M.D., et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arias-de la Rosa I., Escudero-Contreras A., Rodríguez-Cuenca S., Ruiz-Ponce M., Jiménez-Gómez Y., Ruiz-Limón P., Pérez-Sánchez C., Ábalos-Aguilera M.C., Cecchi I., Ortega R., et al. Defective glucose and lipid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis is determined by chronic inflammation in metabolic tissues. J. Intern. Med. 2018;284:61–77. doi: 10.1111/joim.12743. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aron-Wisnewsky J., Tordjman J., Poitou C., Darakhshan F., Hugol D., Basdevant A., Aissat A., Guerre-Millo M., Clément K. Human adipose tissue macrophages: m1 and m2 cell surface markers in subcutaneous and omental depots and after weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009;94:4619–4623. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-0925. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Auguet T., Aragonès G., Guiu-Jurado E., Berlanga A., Curriu M., Martinez S., Alibalic A., Aguilar C., Camara M.L., Hernández E., et al. Adipo/cytokines in atherosclerotic secretomes: increased visfatin levels in unstable carotid plaque. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016;16:149. doi: 10.1186/s12872-016-0320-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

