Characterization of Innovation to Fight Child Mortality: A Systematic Scoping Review
- PMID: 36046259
- PMCID: PMC9421644
- DOI: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604815
Characterization of Innovation to Fight Child Mortality: A Systematic Scoping Review
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to summarize how child mortality-a Sustainable Development Goal stated by the United Nations-has been explicitly addressed in the context of innovations. Methods: A scoping review following the PRISMA-ScR Statement was performed analysing indexed and non-indexed literature. Results: Empirical and non-disruptive innovation in the context of process targeting under-five mortality rate was the main subset of literature included in this article. The increment of literature on innovation in the context of SDGs over the last years denotes its growing importance and even though innovation aiming to reduce child mortality is currently being done, a significant part of it is not published in indexed databases but as grey literature. Conclusion: Empirical, disruptive innovation under a structural approach and empirical, non-disruptive innovation under a project point of view are the main types of innovation addressed in the literature and would be of utmost potential to reduce child mortality rate. A systematic review of the methods used for the measures of evaluation of applied innovations, their quality and results would be of great importance in the future.
Keywords: child mortality; innovation; neonatal mortality rate; scoping review; sustainable development goal; under-five mortality rate.
Copyright © 2022 Costa, Carneiro, Ramalho and Freitas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
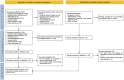
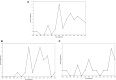
Similar articles
-
Efforts to address the Sustainable Development Goals in older populations: a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2023 Mar 8;23(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15308-4. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36890447 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing and the Sustainable Development Goals: A Scoping Review.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2021 Sep;53(5):568-577. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12675. Epub 2021 May 30. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2021. PMID: 34056841
-
Integrating the United Nations sustainable development goals into higher education globally: a scoping review.Glob Health Action. 2023 Dec 31;16(1):2190649. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2023.2190649. Glob Health Action. 2023. PMID: 36999571 Free PMC article.
-
Death audits and reviews for reducing maternal, perinatal and child mortality.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 25;3(3):CD012982. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012982.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32212268 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping research evidence on perinatal asphyxia within the sustainable development era in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review protocol.Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 30;11(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-02058-4. Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36042525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjegovic-Mikanovic V, Abousbie ZAS, Breckenkamp J, Wenzel H, Broniatowski R, Nelson C, et al. A gap Analysis of SDG 3 and MDG 4/5mortality Health Targets in the Six Arabic Countries of North Africa: Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, and Mauritania. Libyan J Med (2019) 14(1):1607698–6. 10.1080/19932820.2019.1607698 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Available from: www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2015 (Accessed November, 2021).
-
- UNICEF. Indicator 3.2.1: Under-5 Mortality Rate (2019). Available from: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/metadata/files/Metadata-03-02-01.pdf (Accessed November, 2021).
-
- UNICEF. Indicator 3.2.2: Neonatal Mortality Rate (2019). Available from: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/metadata/files/Metadata-03-02-02.pdf (Accessed November, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

