Statins and cognition: Modifying factors and possible underlying mechanisms
- PMID: 36046494
- PMCID: PMC9421063
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.968039
Statins and cognition: Modifying factors and possible underlying mechanisms
Abstract
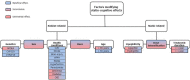
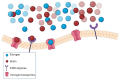
Statins are a class of widely prescribed drugs used to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and important to prevent cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Most statin users are older adults with CVD, who are also at high risk of cognitive decline. It has been suggested that statins can alter cognitive performance, although their positive or negative effects are still debated. With more than 200 million people on statin therapy worldwide, it is crucial to understand the reasons behind discrepancies in the results of these studies. Here, we review the effects of statins on cognitive function and their association with different etiologies of dementia, and particularly, Alzheimer's disease (AD). First, we summarized the main individual and statin-related factors that could modify the cognitive effects of statins. Second, we proposed the underlying mechanisms for the protective and adverse effects of statins on cognitive performance. Finally, we discussed potential causes of discrepancies between studies and suggested approaches to improve future studies assessing the impact of statins on dementia risk and cognitive function.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cognitive function; factors; mechanisms; repurposing; statins.
Copyright © 2022 Jamshidnejad-Tosaramandani, Kashanian, Al-Sabri, Kročianová, Clemensson, Gentreau and Schiöth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alisha K., Tripti S. (2021). Repurposing statins as a potential ligand for estrogen receptor alpha via molecular docking. Ile 5 7–89. 10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00650 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

