Integrated bioinformatic analysis reveals immune molecular markers and potential drugs for diabetic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 36046789
- PMCID: PMC9421304
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.933635
Integrated bioinformatic analysis reveals immune molecular markers and potential drugs for diabetic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
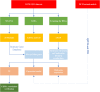
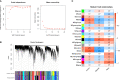
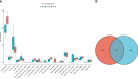
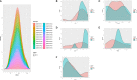
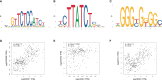
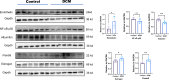
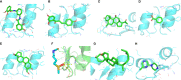
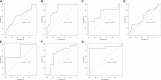
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a pathophysiological condition induced by diabetes mellitus that often causes heart failure (HF). However, their mechanistic relationships remain unclear. This study aimed to identify immune gene signatures and molecular mechanisms of DCM. Microarray data from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database from patients with DCM were subjected to weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) identify co-expression modules. Core expression modules were intersected with the immune gene database. We analyzed and mapped protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks using the STRING database and MCODE and filtering out 17 hub genes using cytoHubba software. Finally, potential transcriptional regulatory factors and therapeutic drugs were identified and molecular docking between gene targets and small molecules was performed. We identified five potential immune biomarkers: proteosome subunit beta type-8 (PSMB8), nuclear factor kappa B1 (NFKB1), albumin (ALB), endothelin 1 (EDN1), and estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1). Their expression levels in animal models were consistent with the changes observed in the datasets. EDN1 showed significant differences in expression in both the dataset and the validation model by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) and Western blotting(WB). Subsequently, we confirmed that the potential transcription factors upstream of EDN1 were PRDM5 and KLF4, as its expression was positively correlated with the expression of the two transcription factors. To repurpose known therapeutic drugs, a connectivity map (CMap) database was retrieved, and nine candidate compounds were identified. Finally, molecular docking simulations of the proteins encoded by the five genes with small-molecule drugs were performed. Our data suggest that EDN1 may play a key role in the development of DCM and is a potential DCM biomarker.
Keywords: bioinformatics; biomarker; diabetes mellitus; diabetic cardiomyopathy; molecular docking; potential drugs.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Zhu, Zhang, Qu, Cheang, Liao, Chen, Zhu, Shi and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewers JS and JL declared a shared affiliation, with no collaboration, with the authors to the handling editor at the time of the review.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

