The psychosocial needs of patients who have chronic kidney disease without kidney replacement therapy: a thematic synthesis of seven qualitative studies
- PMID: 36048367
- PMCID: PMC9700594
- DOI: 10.1007/s40620-022-01437-3
The psychosocial needs of patients who have chronic kidney disease without kidney replacement therapy: a thematic synthesis of seven qualitative studies
Abstract
Background: Limited quantitative data suggests that patients who have chronic kidney disease without kidney replacement therapy (CKD without KRT) may present with psychosocial needs just as patients who have acute kidney injury and are treated by dialysis (AKI stage 3D) do. This systematic review aims to synthesise qualitative research on patients' experiences of CKD without KRT to provide further insight into patients' experience of the healthcare they receive and simultaneously, their psychosocial needs, to inform the development of appropriate psychological interventions.
Methods: The review followed ENTREQ guidelines. PubMed/MEDLINE, PsycINFO, EMBASE and CINAHL were searched in July and August 2021. Qualitative studies in English on the experiences of CKD without KRT care were included in the review. Thematic synthesis was conducted on the findings of the included studies.
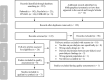
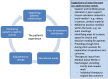
Results: The search identified 231 articles for screening. Eight studies met the inclusion criteria, and one was excluded at the quality assessment stage. The final seven articles [n = 130 patients] were analysed. Five themes on psychosocial needs were developed: addressing patients' CKD-related educational needs, supporting the patient's relationships, honouring the patient's need for control, adjusting to change, and recognising fear of disease and treatment.
Discussion: This review highlights the range of psychosocial needs of patients who have CKD without KRT. There are numerous intervention options that clinicians may develop that could benefit patients and address multiple needs, such as group educational programmes.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Chronic kidney disease without kidney replacement therapy; Psychosocial needs; Psychosocial support.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2021) Chronic kidney disease: assessment and management. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng203. Accessed 2 Mar 2022
-
- Sein K, Damery S, Baharani J, Nicholas J, Combes G. Emotional distress and adjustment in patients with end-stage kidney disease: a qualitative exploration of patient experience in four hospital trusts in the West Midlands. UK PloS One. 2020;15(11):e0241629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241629. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous