Loaded inter-set stretch may selectively enhance muscular adaptations of the plantar flexors
- PMID: 36048793
- PMCID: PMC9436038
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273451
Loaded inter-set stretch may selectively enhance muscular adaptations of the plantar flexors
Abstract
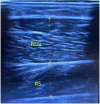
The purpose of this study was to evaluate differences in changes in muscle strength and muscle thickness (MT) of the plantar flexor muscles between traditional resistance training (RT) involving passive rest and RT combined with inter-set stretch in the calf raise exercise. Employing a within-subject design, 21 young, healthy men performed plantar flexion exercises twice per week in both a traditional RT (TRAD) format and combined with a 20-second inter-set stretch (STRETCH). One leg was randomly assigned to the TRAD condition and the contralateral leg performed the STRETCH condition throughout the 8-week study period. Dependent variables included MT of the lateral gastrocnemius (LG), medial gastrocnemius (MG) and the soleus (SOL), and isometric strength of the plantar flexors. Results indicated a potential beneficial hypertrophic effect of STRETCH compared to TRAD for the SOL [0.7 mm, CI90% = (0, 1.6)], while the LG had more ambiguous effects [0.4 mm (-0.4, 1.3)] and MG effects were equivocal [0 mm (-0.6, 0.7)]. In general, LG demonstrated greater standardized growth [z = 1.1 (1, 1.3)] as compared to MG [z = 0.3 (0.2, 0.5)] and SOL [z = 0.3 (0.2, 0.5)]. Measures of isometric strength showed a modest advantage to STRETCH. In conclusion, loaded inter-set stretch may enhance MT of the soleus but effects on the gastrocnemii appear uncertain or unlikely in untrained men; plantar flexor strength appears to be modestly enhanced by the interventional strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: BJS serves on the scientific advisory board of Tonal Corporation, a manufacturer of exercise equipment. Tonal did not provide any funding for the study, nor were they involved in the design, methods, analysis or write-up of the manuscript. This competing interest does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
-
- Antonio J, Gonyea WJ. Muscle fiber splitting in stretch-enlarged avian muscle. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1994. August 01;26(8):973–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

