A rapid RT-LAMP SARS-CoV-2 screening assay for collapsing asymptomatic COVID-19 transmission
- PMID: 36048856
- PMCID: PMC9436079
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273912
A rapid RT-LAMP SARS-CoV-2 screening assay for collapsing asymptomatic COVID-19 transmission
Abstract
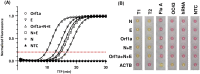
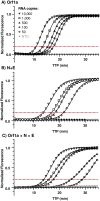
Purpose: To demonstrate the diagnostic performance of rapid SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP assays, comparing the performance of genomic versus sub-genomic sequence target with subsequent application in an asymptomatic screening population.
Methods: RT-LAMP diagnostic specificity (DSe) and sensitivity (DSe) was determined using 114 RT-PCR clinically positive and 88 RT-PCR clinically negative swab samples processed through the diagnostic RT-PCR service within the University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust. A swab-based RT-LAMP SARS-CoV-2 screening programme was subsequently made available to all staff and students at the University of Leicester (Autumn 2020), implemented to ISO 15189:2012 standards using NHS IT infrastructure and supported by University Hospital Leicester via confirmatory NHS diagnostic laboratory testing of RT-LAMP 'positive' samples.
Results: Validation samples reporting a Ct < 20 were detected at 100% DSe and DSp, reducing to 95% DSe (100% DSp) for all samples reporting a Ct < 30 (both genomic dual sub-genomic assays). Advisory screening identified nine positive cases in 1680 symptom free individuals (equivalent to 540 cases per 100,000) with results reported back to participants and feed into national statistics within 48 hours.
Conclusion: This work demonstrates the utility of a rapid RT-LAMP assay for collapsing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in an asymptomatic screening population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Brendish NJ, Poole S, Naidu VV, Mansbridge CT, Norton NJ, Wheeler H, et al.. Clinical impact of molecular point-of-care testing for suspected COVID-19 in hospital (COV-19POC): a prospective, interventional, non-randomised, controlled study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(12):1192–200. Epub 2020/10/12. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30454-9 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

