Cytochromes P450 2C8 and 3A Catalyze the Metabolic Activation of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Masitinib
- PMID: 36048877
- PMCID: PMC10226528
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00057
Cytochromes P450 2C8 and 3A Catalyze the Metabolic Activation of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Masitinib
Abstract
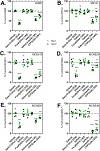
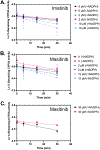
Masitinib is a small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor under investigation for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mastocytosis, and COVID-19. Hepatotoxicity has been reported in some patients while taking masitinib. The liver injury is thought to involve hepatic metabolism of masitinib by cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes to form chemically reactive, potentially toxic metabolites. The goal of the current investigation was to determine the P450 enzymes involved in the metabolic activation of masitinib in vitro. In initial studies, masitinib (30 μM) was incubated with pooled human liver microsomes in the presence of NADPH and potassium cyanide to trap reactive iminium ion metabolites as cyano adducts. Masitinib metabolites and cyano adducts were analyzed using reversed-phase liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The primary active metabolite, N-desmethyl masitinib (M485), and several oxygenated metabolites were detected along with four reactive metabolite cyano adducts (MCN510, MCN524, MCN526, and MCN538). To determine which P450 enzymes were involved in metabolite formation, reaction phenotyping experiments were conducted by incubation of masitinib (2 μM) with a panel of recombinant human P450 enzymes and by incubation of masitinib with human liver microsomes in the presence of P450-selective chemical inhibitors. In addition, enzyme kinetic assays were conducted to determine the relative kinetic parameters (apparent Km and Vmax) of masitinib metabolism and cyano adduct formation. Integrated analysis of the results from these experiments indicates that masitinib metabolic activation is catalyzed primarily by P450 3A4 and 2C8, with minor contributions from P450 3A5 and 2D6. These findings provide further insight into the pathways involved in the generation of reactive, potentially toxic metabolites of masitinib. Future studies are needed to evaluate the impact of masitinib metabolism on the toxicity of the drug in vivo.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03127267 NCT04333108 NCT05441488 NCT05047783 NCT04622865 NCT05449444.
Figures






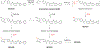
References
-
- Dubreuil P; Letard S; Ciufolini M; Gros L; Humbert M; Casteran N; Borge L; Hajem B; Lermet A; Sippl W; Voisset E; Arock M; Auclair C; Leventhal PS; Mansfield CD; Moussy A; Hermine O Masitinib (AB1010), a potent and selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting KIT. PLoS One 2009, 4, No. e7258. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mora JS; Genge A; Chio A; Estol CJ; Chaverri D; Hernández M; Marín S; Mascias J; Rodriguez GE; Povedano M; Paipa A; Dominguez R; Gamez J; Salvado M; Lunetta C; Ballario C; Riva N; Mandrioli J; Moussy A; Kinet JP; Auclair C; Dubreuil P; Arnold V; Mansfield CD; Hermine O; on behalf of the AB10015 STUDY GROUP. Masitinib as an add-on therapy to riluzole in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a randomized clinical trial. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener 2020, 21, 5–14. - PubMed
-
- Adenis A; Blay JY; Bui-Nguyen B; Bouché O; Bertucci F; Isambert N; Bompas E; Chaigneau L; Domont J; Ray-Coquard I; Blésius A; Van Tine BA; Bulusu VR; Dubreuil P; Mansfield CD; Acin Y; Moussy A; Hermine O; Le Cesne A Masitinib in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) after failure of imatinib: a randomized controlled open-label trial. Ann. Oncol 2014, 25, 1762–1769. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

