A conserved viral amphipathic helix governs the replication site-specific membrane association
- PMID: 36048900
- PMCID: PMC9473614
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010752
A conserved viral amphipathic helix governs the replication site-specific membrane association
Abstract
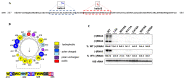
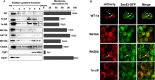
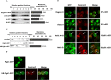
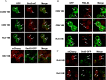
Positive-strand RNA viruses assemble their viral replication complexes (VRCs) on specific host organelle membranes, yet it is unclear how viral replication proteins recognize and what motifs or domains in viral replication proteins determine their destinations. We show here that an amphipathic helix, helix B in replication protein 1a of brome mosaic virus (BMV), is necessary for 1a's localization to the nuclear endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane where BMV assembles its VRCs. Helix B is also sufficient to target soluble proteins to the nuclear ER membrane in yeast and plant cells. We further show that an equivalent helix in several plant- and human-infecting viruses of the Alsuviricetes class targets fluorescent proteins to the organelle membranes where they form their VRCs, including ER, vacuole, and Golgi membranes. Our work reveals a conserved helix that governs the localization of VRCs among a group of viruses and points to a possible target for developing broad-spectrum antiviral strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An unrecognized function for COPII components in recruiting the viral replication protein BMV 1a to the perinuclear ER.J Cell Sci. 2016 Oct 1;129(19):3597-3608. doi: 10.1242/jcs.190082. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27539921
-
Brome mosaic virus RNA replication proteins 1a and 2a colocalize and 1a independently localizes on the yeast endoplasmic reticulum.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10303-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10303-10309.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559348 Free PMC article.
-
Cowpea chlorotic mottle bromovirus replication proteins support template-selective RNA replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 26;13(12):e0208743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208743. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30586378 Free PMC article.
-
Bromovirus-induced remodeling of host membranes during viral RNA replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2014 Dec;9:104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.09.018. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2014. PMID: 25462441 Review.
-
Brome mosaic virus RNA replication: revealing the role of the host in RNA virus replication.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2003;41:77-98. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.41.052002.095717. Epub 2003 Mar 10. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2003. PMID: 12651962 Review.
Cited by
-
Manipulation of the Cellular Membrane-Cytoskeleton Network for RNA Virus Replication and Movement in Plants.Viruses. 2023 Mar 14;15(3):744. doi: 10.3390/v15030744. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five questions on the cell-to-cell movement of Orthotospoviruses.BBA Adv. 2024 Oct 16;6:100124. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2024.100124. eCollection 2024. BBA Adv. 2024. PMID: 39498475 Free PMC article.
-
Tobacco Mosaic Virus Movement: From Capsid Disassembly to Transport Through Plasmodesmata.Viruses. 2025 Jan 31;17(2):214. doi: 10.3390/v17020214. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40006969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a membrane-associated element (MAE) in the C-terminal region of SARS-CoV-2 nsp6 that is essential for viral replication.J Virol. 2024 May 14;98(5):e0034924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00349-24. Epub 2024 Apr 19. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38639488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- COVID Live Update: 229,431,285 Cases and 4,708,052 Deaths from the Coronavirus—Worldometer. [cited 19 Sep 2021]. Available: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

