Personal attenuation ratings versus derated noise reduction ratings for hearing protection devices
- PMID: 36050158
- PMCID: PMC12070270
- DOI: 10.1121/10.0013418
Personal attenuation ratings versus derated noise reduction ratings for hearing protection devices
Abstract
National and international regulatory and consensus standards setting bodies have previously proposed derating hearing protector ratings to provide a better match between ratings determined in a laboratory and the real-world measurements of attenuation for workers. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has proposed a derating scheme that depends upon the type of protector. This paper examines four real-world studies where personal attenuation ratings (PARs) were measured at least twice, before and after an intervention in earplug fitting techniques. Results from these studies indicate that individualized earplug fitting training dramatically improves a worker's achieved PAR value. Additionally, derating schemes fail to accurately predict the majority of achieved PARs. Because hearing protector fit testing systems are now readily available for use in the workplace, personal attenuation ratings provide a better estimate of worker noise exposures and are able to identify those persons who need additional instruction in fitting hearing protection devices.
Figures




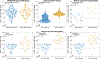
References
-
- ANSI (1974). ANSI S3.19–1974, Acoustical Society of America Standard Method for the Measurement of Real-Ear Protection of Hearing Protectors and Physical Attenuation of Earmuffs. ANSI S3.19–1974, Accredited Standards Committee S3, Noise ((American National Standards Institute, New York: ).
-
- ANSI (1997). ANSI 12.6–1997, American National Standard Methods for Measuring the Real-Ear Attenuation of Hearing Protectors, ANSI 12.6–1997, Accredited Standards Committee S12, Noise (American National Standards Institute, New York: ).
-
- ANSI (2008). ANSI/ASA 12.6–2008, American National Standard Methods for Measuring the Real-Ear Attenuation of Hearing Protectors, ANSI/ASA 12.6–2008, Accredited Standards Committee S12, Noise American NationalStandards Institute, New York: ).
-
- ANSI (2018). ASA/ANSI S12.71–2018, American National Standard Methods of Estimating Effective A-weighted Sound Pressure Levels When Hearing Protectors are Worn, ASA/ANSI 12.68–2007 (R2020), Accredited Standards Committee S12, Noise (American National Standards Institute, New York: ).
-
- ANSI (2020). ASA/ANSI 12.68–2007 (R2020), American National Standard Performance Criteria for Systems that Estimate the Attenuation of Passive Hearing Protectors for Individual Users, ASA/ANSI S12.71–2018, Accredited Standards Committee S12, Noise (American National Standards Institute, New York: ).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

