Lactate metabolism in human health and disease
- PMID: 36050306
- PMCID: PMC9434547
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01151-3
Lactate metabolism in human health and disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: Lactate metabolism in human health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Oct 31;7(1):372. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01206-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36316308 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
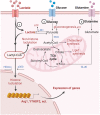
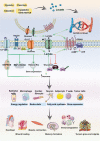
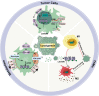
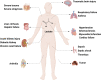
The current understanding of lactate extends from its origins as a byproduct of glycolysis to its role in tumor metabolism, as identified by studies on the Warburg effect. The lactate shuttle hypothesis suggests that lactate plays an important role as a bridging signaling molecule that coordinates signaling among different cells, organs and tissues. Lactylation is a posttranslational modification initially reported by Professor Yingming Zhao's research group in 2019. Subsequent studies confirmed that lactylation is a vital component of lactate function and is involved in tumor proliferation, neural excitation, inflammation and other biological processes. An indispensable substance for various physiological cellular functions, lactate plays a regulatory role in different aspects of energy metabolism and signal transduction. Therefore, a comprehensive review and summary of lactate is presented to clarify the role of lactate in disease and to provide a reference and direction for future research. This review offers a systematic overview of lactate homeostasis and its roles in physiological and pathological processes, as well as a comprehensive overview of the effects of lactylation in various diseases, particularly inflammation and cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

