DNA-PAINT MINFLUX nanoscopy
- PMID: 36050490
- PMCID: PMC9467913
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-022-01577-1
DNA-PAINT MINFLUX nanoscopy
Abstract
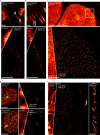
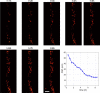
MINimal fluorescence photon FLUXes (MINFLUX) nanoscopy, providing photon-efficient fluorophore localizations, has brought about three-dimensional resolution at nanometer scales. However, by using an intrinsic on-off switching process for single fluorophore separation, initial MINFLUX implementations have been limited to two color channels. Here we show that MINFLUX can be effectively combined with sequentially multiplexed DNA-based labeling (DNA-PAINT), expanding MINFLUX nanoscopy to multiple molecular targets. Our method is exemplified with three-color recordings of mitochondria in human cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.W.H. holds shares of Abberior Instruments and has revenues through MINFLUX patents held by the Max Planck Society. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

