Network metrics, structural dynamics and density functional theory calculations identified a novel Ursodeoxycholic Acid derivative against therapeutic target Parkin for Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 36051887
- PMCID: PMC9399899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.017
Network metrics, structural dynamics and density functional theory calculations identified a novel Ursodeoxycholic Acid derivative against therapeutic target Parkin for Parkinson's disease
Abstract
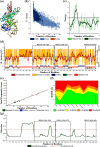
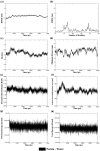
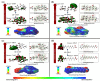
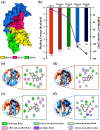
Parkinson's disease (PD) has been designated as one of the priority neurodegenerative disorders worldwide. Although diagnostic biomarkers have been identified, early onset detection and targeted therapy are still limited. An integrated systems and structural biology approach were adopted to identify therapeutic targets for PD. From a set of 49 PD associated genes, a densely connected interactome was constructed. Based on centrality indices, degree of interaction and functional enrichments, LRRK2, PARK2, PARK7, PINK1 and SNCA were identified as the hub-genes. PARK2 (Parkin) was finalized as a potent theranostic candidate marker due to its strong association (score > 0.99) with α-synuclein (SNCA), which directly regulates PD progression. Besides, modeling and validation of Parkin structure, an extensive virtual-screening revealed small (commercially available) inhibitors against Parkin. Molecule-258 (ZINC5022267) was selected as a potent candidate based on pharmacokinetic profiles, Density Functional Theory (DFT) energy calculations (ΔE = 6.93 eV) and high binding affinity (Binding energy = -6.57 ± 0.1 kcal/mol; Inhibition constant = 15.35 µM) against Parkin. Molecular dynamics simulation of protein-inhibitor complexes further strengthened the therapeutic propositions with stable trajectories (low structural fluctuations), hydrogen bonding patterns and interactive energies (>0kJ/mol). Our study encourages experimental validations of the novel drug candidate to prevent the auto-inhibition of Parkin mediated ubiquitination in PD.
Keywords: ADMET, Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity; AI, Artificial Intelligence; BBB, Blood Brain Barrier; Biomarker; CS, Confidence Scores; DFT, Density Functional Theory; DL, Deep Learning; Docking; FEA, Functional Enrichment Analysis; GI, Gasto-Intestinal; GIN, Gene Interaction Network; GO, Gene Ontology; HOMO, Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital; IC, Inhibition Constant; LB, Lewy Bodies; LD, Lethal Dose; LUMO, Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital; Ligand optimization; MDS, Molecular Dynamics Simulation; ML, Machine Learning; MMP, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential; Neurodegenerative disorder; PD, Parkinson's Disease; RMSD, Root Means Square Deviation; RMSF, Root Means Square Fluctuation; Rg, Radius of Gyration; SNpc, Substantia Nigra pars compacta; Simulation; Systems biology; TPSA, Total Polar Surface Area; UDCA, Ursodeoxycholic Acid.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Research Network of Computational and Structural Biotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
