Portulaca oleracea L. extracts alleviate 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice
- PMID: 36051905
- PMCID: PMC9424637
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.986943
Portulaca oleracea L. extracts alleviate 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice
Abstract
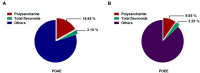
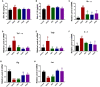
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic allergic skin disease characterized clinically by severe skin lesions and pruritus. Portulaca oleracea L. (PO) is a resourceful plant with homologous properties in medicine and food. In this study, we used two different methods to extract PO, and compared the therapeutic effects of PO aqueous extract (POAE) and PO ultrasound-assisted ethanol extract (POEE) on 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-induced AD mice. The results showed that in POAE and POEE, the extraction rates of polysaccharides were 16.95% and 9.85%, while the extraction rates of total flavonoids were 3.15% and 3.25%, respectively. Compared with AD mice, clinical symptoms such as erythema, edema, dryness and ulceration in the back and left ear were alleviated, and pruritus behavior was reduced after POAE and POEE treatments. The thickness of the skin epidermis was thinned, the density of skin nerve fibers labeled with protein gene product 9.5 (PGP9.5) was decreased, and mast cell infiltration was reduced. There was a decrease in blood lymphocytes, eosinophils and basophils, a significant decrease in spleen index and a noticeable decrease in serum immunoglobulin E (Ig E). POEE significantly reduced the concentration of the skin pruritic factor interleukin (Il)-31. POAE and POEE reduced the concentration of skin histamine (His), down-regulated mRNA expression levels of interferon-γ (Ifnγ), tumor necrosis factor-α (Tnf-α), thymic stromal lymphopoietin (Tslp) and Il-4, with an increase of Filaggrin (Flg) and Loricrin (Lor) in skin lesions. These results suggested that POAE and POEE may inhibit atopic response and alleviate the clinical symptoms of AD by inhibiting the expression of immune cells, inflammatory mediators and cytokines. PO may be a potential effective drug for AD-like diseases.
Keywords: 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB); Portulaca oleracea L.; anti-inflammatory; anti-pruritic; atopic dermatitis; immunomodulation.
Copyright © 2022 Lv, Huang, Li, Gong, Sun, Mao and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Probiotic-fermented Portulaca oleracea L. alleviated DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Sep 15;313:116613. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116613. Epub 2023 May 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37156447
-
Deacetylasperulosidic Acid Ameliorates Pruritus, Immune Imbalance, and Skin Barrier Dysfunction in 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis NC/Nga Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 25;23(1):226. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010226. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008651 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-atopic effect of Viola yedoensis ethanol extract against 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin dysfunction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;280:114474. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114474. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34332065
-
Fermented Morinda citrifolia (Noni) Alleviates DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice through Modulating Immune Balance and Skin Barrier Function.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 18;12(1):249. doi: 10.3390/nu12010249. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31963703 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Characteristics and Anti-Inflammatory, Immunoregulatory, and Antioxidant Effects of Portulaca oleracea L.: A Comprehensive Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Aug 31;2023:2075444. doi: 10.1155/2023/2075444. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37693918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Mast Cell Degranulation in Atopic Dermatitis by Celastrol through Suppressing MRGPRX2.Dis Markers. 2023 Jan 18;2023:9049256. doi: 10.1155/2023/9049256. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 36712922 Free PMC article.
-
Portulaca oleracea L. polysaccharide inhibits ovarian cancer via inducing ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 19;16(6):5108-5122. doi: 10.18632/aging.205608. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38503553 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of purslane extract on immuno-antioxidant status, intestinal barrier, and microbiota of chicks after experimental infection with Escherichia coli O78.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun;104(6):105106. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105106. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40245541 Free PMC article.
-
Taraxacum mongolicum Ameliorates DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in Mice by Regulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, MAPK, and JAK/STAT/TSLP Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 9;26(14):6601. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146601. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724851 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary purslane modulates gut microbiota and fecal metabolites in aging rats.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1549853. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1549853. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40177479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC phases one and three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. (2006) 368:733–43. 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69283-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

