High baseline expression of IL-6 and IL-10 decreased CCR7 B cells in individuals with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection during BNT162b2 vaccination
- PMID: 36052060
- PMCID: PMC9425053
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.946770
High baseline expression of IL-6 and IL-10 decreased CCR7 B cells in individuals with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection during BNT162b2 vaccination
Abstract
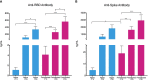
The current pandemic generated by SARS-CoV-2 has led to mass vaccination with different biologics that have shown wide variations among human populations according to the origin and formulation of the vaccine. Studies evaluating the response in individuals with a natural infection before vaccination have been limited to antibody titer analysis and evaluating a few humoral and cellular response markers, showing a more rapid and intense humoral response than individuals without prior infection. However, the basis of these differences has not been explored in depth. In the present work, we analyzed a group of pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines, antibody titers, and cell populations in peripheral blood of individuals with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection using BNT162b2 biologic. Our results suggest that higher antibody concentration in individuals with an earlier disease could be generated by higher production of plasma cells to the detriment of the presence of memory B cells in the bloodstream, which could be related to the high baseline expression of cytokines (IL-6 and IL-10) before vaccination.
Keywords: BNT162b2; CCR7 B cells; Interleukin 10; Interleukin 6; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Ponciano-Gómez, Valle-Solis, Campos-Aguilar, Jijón-Lorenzo, Herrera-Cogco, Ramos-Alor, Bazán-Mendez, Cervantes, Ávila-García, Aguilar, Texale, Tapia-Sánchez, Duarte-Martínez, Olivas-Quintero, Sigrist-Flores, Gallardo-Ortíz, Villalobos-Molina, Méndez-Cruz, Jimenez-Flores, Santos-Argumedo, Luna-Arias, Romero-Ramírez, Rosales-García and Avendaño-Borromeo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sokolowska M, Lukasik ZM, Agache I, Akdis CA, Akdis D, Akdis M, et al. Immunology of COVID-19: Mechanisms, clinical outcome, diagnostics, and perspectives–a report of the european academy of allergy and clinical immunology (EAACI). Allergy Eur J Allergy Clin Immunol (2020) 75(10):2445–76. doi: 10.1111/all.14462 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

