Protective effect of quercetin on cadmium-induced renal apoptosis through cyt-c/caspase-9/caspase-3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 36052148
- PMCID: PMC9425064
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.990993
Protective effect of quercetin on cadmium-induced renal apoptosis through cyt-c/caspase-9/caspase-3 signaling pathway
Abstract
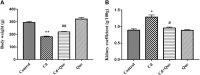
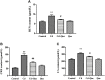
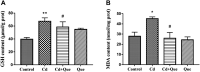
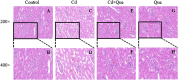
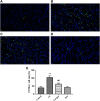
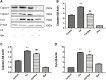
Cadmium (Cd), a heavy metal, has harmful effects on animal and human health, and it can also obviously induce cell apoptosis. Quercetin (Que) is a flavonoid compound with antioxidant and other biological activities. To investigate the protective effect of Que on Cd-induced renal apoptosis in rats. 24 male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups. They were treated as follows: control group was administered orally with normal saline (10 ml/kg); Cd group was injected with 2 mg/kg CdCl2 intraperitoneally; Cd + Que group was injected with 2 mg/kg CdCl2 and intragastric administration of Que (100 mg/kg); Que group was administered orally with Que (100 mg/kg). The experimental results showed that the body weight of Cd-exposed rats significantly decreased and the kidney coefficient increased. In addition, Cd significantly increased the contents of Blood Urea Nitrogen, Creatinine and Uric acid. Cd also increased the glutathione and malondialdehyde contents in renal tissues. The pathological section showed that Cd can cause pathological damages such as narrow lumen and renal interstitial congestion. Cd-induced apoptosis of kidney, which could activate the mRNA and protein expression levels of Cyt-c, Caspase-9 and Caspase-3 were significantly increased. Conversely, Que significantly reduces kidney damage caused by Cd. Kidney pathological damage was alleviated by Que. Que inhibited Cd-induced apoptosis and decreased Cyt-c, Caspase-9 and Caspase-3 proteins and mRNA expression levels. To sum up, Cd can induce kidney injury and apoptosis of renal cells, while Que can reduce Cd-induced kidney damage by reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting apoptosis. These results provide a theoretical basis for the clinical application of Que in the prevention and treatment of cadmium poisoning.
Keywords: apoptosis; cadmium; kidney injury; oxidative stress; quercetin.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Ding, Ye, Wang, Yu, Yan, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carrasco-Torres G., Monroy-Ramírez H. C., Martínez-Guerra A. A., Baltiérrez-Hoyos R., Romero-Tlalolini M., Villa-Treviño S., et al. (2017). Quercetin reverses rat liver preneoplastic lesions induced by chemical carcinogenesis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 4674918. 10.1155/2017/4674918 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choe J. Y., Park K. Y., Kim S. K. (2015). Oxidative stress by monosodium urate crystals promotes renal cell apoptosis through mitochondrial caspase-dependent pathway in human embryonic kidney 293 cells: Mechanism for urate-induced nephropathy. Apoptosis 20 (1), 38–49. 10.1007/s10495-014-1057-1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

