Renal denervation in the antihypertensive arsenal - knowns and known unknowns
- PMID: 36052518
- PMCID: PMC10010701
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003171
Renal denervation in the antihypertensive arsenal - knowns and known unknowns
Erratum in
-
Renal denervation in the antihypertensive arsenal - knowns and known unknowns: Erratum.J Hypertens. 2022 Nov 1;40(11):2322. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003309. J Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 36205018 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
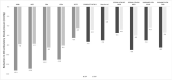
Even though it has been more than a decade since renal denervation (RDN) was first used to treat hypertension and an intense effort on researching this therapy has been made, it is still not clear how RDN fits into the antihypertensive arsenal. There is no question that RDN lowers blood pressure (BP), it does so to an extent at best corresponding to one antihypertensive drug. The procedure has an excellent safety record. However, it remains clinically impossible to predict whose BP responds to RDN and whose does not. Long-term efficacy data on BP reduction are still unconvincing despite the recent results in the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED trial; experimental studies indicate that reinnervation is occurring after RDN. Although BP is an acceptable surrogate endpoint, there is complete lack of outcome data with RDN. Clear indications for RDN are lacking although patients with resistant hypertension, those with documented increase in activity of the sympathetic system and perhaps those who desire to take fewest medication may be considered.
Copyright © 2022 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Chirag Bavishi: None.
Jana Brguljan: None.
Michel Burnier: Consulting fees from Medtronic, Servier, Menarini, Bayer.
Stephan Dobner: None.
Fernando Elijovich: None.
Keith C. Ferdinand: None.
Sverre Kjeldsen: Within the past 3 years: Lecture honoraria from Getz, Vector-Intas, Merck KGaA and Sanofi-Aventis.
Cheryl L. Laffer: None.
Franz H. Messerli: Honoraria from Medtronic, Menarini, Krka, Ipca.
C. Venkata S. Ram: None.
Emrush Rexhaj: None.
Luis M. Ruilope: None.
Evgeniya V. Shalaeva: None.
George C.M. Siontis: None.
Jan A. Staessen: None.
Stephen C. Textor: Section editor, UpToDate, DSMB: Sentien Biotherapeutics, No conflict of interest.
Wanpen Vongpatanasin: None.
Liffert Vogt: None.
Massimo Volpe: Scientific collaboration Agreement between Medtronic and Dept.of Clinical & Molecular Medicine, Univ of Rome Sapienza; Steering Committee for the Denex EU study sponsored by Kalos Medical, SK
Jiguang Wang: Jiguang Wang reports having received lecture and consulting fees from Novartis, Omron, Servier and Viatris
Bryan Williams: None.
Figures

References
-
- Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Böhm M, et al. . Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 376:1903–1909. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW, D’Agostino R, Flack JM, Katzen BT, et al. . A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med 2014; 370:1393–1401. - PubMed
-
- Rosa J, Widimský P, Toušek P, Petrák O, Čurila K, Waldauf P, et al. . Randomized comparison of renal denervation versus intensified pharmacotherapy including spironolactone in true-resistant hypertension: six-month results from the Prague-15 study. Hypertension 2015; 65:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Azizi M, Sapoval M, Gosse P, Monge M, Bobrie G, Delsart P, et al. . Optimum and stepped care standardised antihypertensive treatment with or without renal denervation for resistant hypertension (DENERHTN): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015; 385:1957–1965. - PubMed
-
- Townsend RR, Mahfoud F, Kandzari DE, Kario K, Pocock S, Weber MA, et al. . Catheter-based renal denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED): a randomised, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet 2017; 390:2160–2170. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

