Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor enhances eribulin-induced DNA damage in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 36053154
- PMCID: PMC9746063
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15558
Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor enhances eribulin-induced DNA damage in colorectal cancer
Abstract
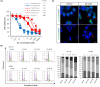
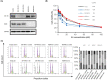
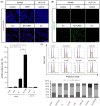
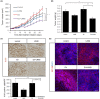
Microtubule targeting agents (MTAs) such as taxanes are broadly used for the treatment of patients with cancer. Although MTAs are not effective for treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC), preclinical studies suggest that a subset of patients with CRC, especially those with cancers harboring the BRAF mutation, could benefit from such agents. However, two MTAs, eribulin (Eri) and vinorelbine, have shown limited clinical efficacy. Here, we report that insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) signaling is involved in Eri resistance. Using CRC cell lines, we showed that Eri induces activation and subsequent translocation of IGF-1R to the nucleus. When the activation and/or nuclear translocation of IGF-1R was inhibited, Eri induced DNA damage and enhanced G2 /M arrest. In a xenograft model using the Eri-resistant SW480 cell line, the combination of Eri and the IGF-1R inhibitor linsitinib suppressed tumor growth more efficiently than either single agent. Thus, our results indicated that combination dosing with Eri and an IGF-1R inhibitor could overcome Eri resistance and offer a therapeutic opportunity in CRC.
Keywords: IGF-1R; ROS; colorectal cancer; eribulin; microtubule.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


References
-
- WHO cancer today (2018). Accessed February 1, 2022. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home
-
- Vecchione L, Gambino V, Raaijmakers J, et al. A vulnerability of a subset of colon cancers with potential clinical utility. Cell. 2016;165(2):317‐330. - PubMed
-
- Pollak M. Insulin and insulin‐like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(12):915‐928. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

