Multiple-site decontamination regimen decreases acquired infection incidence in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 36053369
- PMCID: PMC9438389
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-022-01057-x
Multiple-site decontamination regimen decreases acquired infection incidence in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: Among strategies that aimed to prevent acquired infections (AIs), selective decontamination regimens have been poorly studied in the COVID-19 setting. We assessed the impact of a multiple-site decontamination (MSD) regimen on the incidence of bloodstream infections (BSI) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) in COVID-19 patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
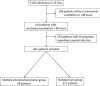
Methods: We performed an ancillary analysis of a multicenter retrospective observational study in 15 ICUs in western France. In addition to standard-care (SC), 3 ICUs used MSD, a variant of selective digestive decontamination, which consists of the administration of topical antibiotics four times daily in the oropharynx and the gastric tube, chlorhexidine body wash and a 5-day nasal mupirocin course. AIs were compared between the 3 ICUs using MSD (MSD group) and the 12 ICUs using SC.
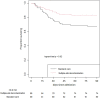
Results: During study period, 614 of 1158 COVID-19 patients admitted in our ICU were intubated for at least 48 h. Due to missing data in 153 patients, 461 patients were finally included of whom 89 received MSD. There were 34 AIs in the MSD group (2117 patient-days), as compared with 274 AIs in the SC group (8957 patient-days) (p < 0.001). MSD was independently associated with a lower risk of AI (IRR = 0.56 [0.38-0.83]; p = 0.004) (Table 2). When the same model was used for each site of infection, MSD remained independently associated with a lower risk of VAP (IRR = 0.52 [0.33-0.89]; p = 0.005) but not of BSI (IRR = 0.58, [0.25-1.34], p = 0.21). Hospital mortality was lower in the MSD group (16.9% vs 30.1%, p = 0.017).
Conclusions: In ventilated COVID-19 patients, MSD was independently associated with lower AI incidence.
Keywords: Bacteremia; COVID-19; Chlorhexidine; Critical care; Mortality; Mupirocin; Pneumonia; Selective digestive decontamination.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Rouzé A, Martin-Loeches I, Povoa P, Makris D, Artigas A, Bouchereau M, et al. Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the incidence of ventilator-associated lower respiratory tract infections: a European multicenter cohort study. Intensive Care Med févr. 2021;47(2):188–198. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06323-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tabah A, Koulenti D, Laupland K, Misset B, Valles J, Bruzzi de Carvalho F, et al. Characteristics and determinants of outcome of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections in intensive care units: the EUROBACT International Cohort Study. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(12):1930–1945. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2695-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources