Bedaquiline-Pretomanid-Linezolid Regimens for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- PMID: 36053506
- PMCID: PMC9490302
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2119430
Bedaquiline-Pretomanid-Linezolid Regimens for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: The bedaquiline-pretomanid-linezolid regimen has been reported to have 90% efficacy against highly drug-resistant tuberculosis, but the incidence of adverse events with 1200 mg of linezolid daily has been high. The appropriate dose of linezolid and duration of treatment with this agent to minimize toxic effects while maintaining efficacy against highly drug-resistant tuberculosis are unclear.
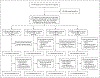
Methods: We enrolled participants with extensively drug-resistant (XDR) tuberculosis (i.e., resistant to rifampin, a fluoroquinolone, and an aminoglycoside), pre-XDR tuberculosis (i.e., resistant to rifampin and to either a fluoroquinolone or an aminoglycoside), or rifampin-resistant tuberculosis that was not responsive to treatment or for which a second-line regimen had been discontinued because of side effects. We randomly assigned the participants to receive bedaquiline for 26 weeks (200 mg daily for 8 weeks, then 100 mg daily for 18 weeks), pretomanid (200 mg daily for 26 weeks), and daily linezolid at a dose of 1200 mg for 26 weeks or 9 weeks or 600 mg for 26 weeks or 9 weeks. The primary end point in the modified intention-to-treat population was the incidence of an unfavorable outcome, defined as treatment failure or disease relapse (clinical or bacteriologic) at 26 weeks after completion of treatment. Safety was also evaluated.
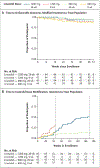
Results: A total of 181 participants were enrolled, 88% of whom had XDR or pre-XDR tuberculosis. Among participants who received bedaquiline-pretomanid-linezolid with linezolid at a dose of 1200 mg for 26 weeks or 9 weeks or 600 mg for 26 weeks or 9 weeks, 93%, 89%, 91%, and 84%, respectively, had a favorable outcome; peripheral neuropathy occurred in 38%, 24%, 24%, and 13%, respectively; myelosuppression occurred in 22%, 15%, 2%, and 7%, respectively; and the linezolid dose was modified (i.e., interrupted, reduced, or discontinued) in 51%, 30%, 13%, and 13%, respectively. Optic neuropathy developed in 4 participants (9%) who had received linezolid at a dose of 1200 mg for 26 weeks; all the cases resolved. Six of the seven unfavorable microbiologic outcomes through 78 weeks of follow-up occurred in participants assigned to the 9-week linezolid groups.
Conclusions: A total of 84 to 93% of the participants across all four bedaquiline-pretomanid-linezolid treatment groups had a favorable outcome. The overall risk-benefit ratio favored the group that received the three-drug regimen with linezolid at a dose of 600 mg for 26 weeks, with a lower incidence of adverse events reported and fewer linezolid dose modifications. (Funded by the TB Alliance and others; ZeNix ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03086486.).
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Linezolid for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis.N Engl J Med. 2022 Sep 1;387(9):842-843. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2208554. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 36053511 No abstract available.
-
Regimens for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jan 12;388(2):189. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2213970. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 36630636 No abstract available.
-
Regimens for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jan 12;388(2):190. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2213970. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 36630637 No abstract available.
-
Regimens for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jan 12;388(2):190-191. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2213970. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 36630638 No abstract available.
-
Tuberkulose: Neue, wirksame Reserve-Kombi.MMW Fortschr Med. 2023 Oct;165(Suppl 3):28. doi: 10.1007/s15006-023-3082-x. MMW Fortschr Med. 2023. PMID: 37857959 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
Mit Sensor in der Lungenarterie besser leben.MMW Fortschr Med. 2023 Oct;165(Suppl 3):28-30. doi: 10.1007/s15006-023-3081-y. MMW Fortschr Med. 2023. PMID: 37857960 Review. German. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2021. October 14, 2021 (https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021).
-
- Pym AS, Diacon AH, Tang S-J, et al. Bedaquiline in the treatment of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur Respir J 2016;47:564–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
