de novo variant calling identifies cancer mutation signatures in the 1000 Genomes Project
- PMID: 36054329
- PMCID: PMC9771978
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.24455
de novo variant calling identifies cancer mutation signatures in the 1000 Genomes Project
Abstract
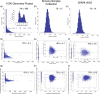
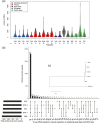
Detection of de novo variants (DNVs) is critical for studies of disease-related variation and mutation rates. To accelerate DNV calling, we developed a graphics processing units-based workflow. We applied our workflow to whole-genome sequencing data from three parent-child sequenced cohorts including the Simons Simplex Collection (SSC), Simons Foundation Powering Autism Research (SPARK), and the 1000 Genomes Project (1000G) that were sequenced using DNA from blood, saliva, and lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs), respectively. The SSC and SPARK DNV callsets were within expectations for number of DNVs, percent at CpG sites, phasing to the paternal chromosome of origin, and average allele balance. However, the 1000G DNV callset was not within expectations and contained excessive DNVs that are likely cell line artifacts. Mutation signature analysis revealed 30% of 1000G DNV signatures matched B-cell lymphoma. Furthermore, we found variants in DNA repair genes and at Clinvar pathogenic or likely-pathogenic sites and significant excess of protein-coding DNVs in IGLL5; a gene known to be involved in B-cell lymphomas. Our study provides a new rapid DNV caller for the field and elucidates important implications of using sequencing data from LCLs for reference building and disease-related projects.
Keywords: 1000 Genomes Project; GPU accelerated workflow; Simons Simplex Collection; cell line artifacts; de novo variants.
© 2022 The Authors. Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Pankaj Vats, Marc A. West, George Vacek, and Timothy T. Harkins are full time employees of NVIDIA.
Figures


References
-
- Alexandrov, L. B. , Nik‐Zainal, S. , Wedge, D. C. , Aparicio, S. A. , Behjati, S. , Biankin, A. V. , Bignell, G. R. , Bolli, N. , Borg, A. , Børresen‐Dale, A. L. , Boyault, S. , Burkhardt, B. , Butler, A. P. , Caldas, C. , Davies, H. R. , Desmedt, C. , Eils, R. , Eyfjörd, J. E. , Foekens, J. A. , … Stratton, M. R. (2013). Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature, 500(7463), 415–421. 10.1038/nature12477 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen, A. S. , Berkovic, S. F. , Cossette, P. , Delanty, N. , Dlugos, D. , Eichler, E. E. , Epstein, M. P. , Glauser, T. , Goldstein, D. B. , Han, Y. , Heinzen, E. L. , Hitomi, Y. , Howell, K. B. , Johnson, M. R. , Kuzniecky, R. , Lowenstein, D. H. , Lu, Y. F. , … Winawer, M. R. , Epi4K Consortium, Epilepsy Phenome/Genome Project . (2013). De novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathies. Nature, 501(7466), 217–221. 10.1038/nature12439 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- An, J. Y. , Lin, K. , Zhu, L. , Werling, D. M. , Dong, S. , Brand, H. , Wang, H. Z. , Zhao, X. , Schwartz, G. B. , Collins, R. L. , Currall, B. B. , Dastmalchi, C. , Dea, J. , Duhn, C. , Gilson, M. C. , Klei, L. , Liang, L. , Markenscoff‐Papadimitriou, E. , Pochareddy, S. , … Sanders, S. J. (2018). Genome‐wide de novo risk score implicates promoter variation in autism spectrum disorder. Science , 362(6420). 10.1126/science.aat6576 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Besenbacher, S. , Liu, S. , Izarzugaza, J. M. , Grove, J. , Belling, K. , Bork‐Jensen, J. , Huang, S. , Als, T. D. , Li, S. , Yadav, R. , Rubio‐García, A. , Lescai, F. , Demontis, D. , Rao, J. , Ye, W. , Mailund, T. , Friborg, R. M. , Pedersen, C. N. , Xu, R. , … Rasmussen, S. (2015). Novel variation and de novo mutation rates in population‐wide de novo assembled Danish trios. Nature Communications, 6, 5969. 10.1038/ncomms6969 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

