Lithium produces bi-directionally regulation of mood disturbance, acts synergistically with anti-depressive/-manic agents, and did not deteriorate the cognitive impairment in murine model of bipolar disorder
- PMID: 36055984
- PMCID: PMC9440114
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-02087-6
Lithium produces bi-directionally regulation of mood disturbance, acts synergistically with anti-depressive/-manic agents, and did not deteriorate the cognitive impairment in murine model of bipolar disorder
Abstract
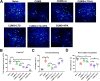
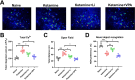
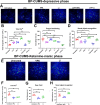
Lithium (Li) is a well-established mood disorder treatment and may be neuroprotective. Bi-directional regulation (i.e. affecting manic symptoms and depressive symptoms) by Li has not been demonstrated. This study explored: (1) bidirectional regulation by Li in murine models of depression, mania, and bipolar disorder (BP); and (2) potential Li synergism with antidepressant/anti-mania agents. The chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) and ketamine-induced mania (KM) models were used. These methods were used in series to produce a BP model. In vivo two-photon imaging was used to visualize Ca2+ activity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Depressiveness, mania, and cognitive function were assessed with the forced swim task (FST), open field activity (OFA) task, and novel object recognition task, respectively. In CUMS mice, Ca2+ activity was increased strongly by Li and weakly by lamotrigine (LTG) or valproate (VPA), and LTG co-administration reduced Li and VPA monotherapy effects; depressive immobility in the FST was attenuated by Li or LTG, and attenuated more strongly by LTG-VPA or LTG-Li; novel object exploration was increased strongly by Li and weakly by LTG-Li, and reduced by LTG, VPA, or LTG-VPA. In KM mice, Li or VPA attenuated OFA mania symptoms and normalized Ca2+ activity partially; Li improved cognitive function while VPA exacerbated the KM alteration. These patterns were replicated in the respective BP model phases. Lithium had bi-directional, albeit weak, mood regulation effects and a cognitive supporting effect. Li co-administration with antidepressant/-manic agents enhanced mood-regulatory efficacy while attenuating their cognitive-impairing effects.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lithium bidirectionally regulates depression- and mania-related brain functional alterations without worsening cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Sep 15;13:963005. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.963005. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36186884 Free PMC article.
-
[Antipsychotics in bipolar disorders].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):417-24. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95456-5. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627046 Review. French.
-
Effects of mood-stabilizing drugs on dendritic outgrowth and synaptic protein levels in primary hippocampal neurons.Bipolar Disord. 2015 May;17(3):278-90. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12262. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Bipolar Disord. 2015. PMID: 25307211
-
Antidepressant effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is not impaired by intake of lithium or antiepileptic drugs.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021 Oct;271(7):1245-1253. doi: 10.1007/s00406-021-01287-3. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34218305 Free PMC article.
-
[Guidelines for the prescription of mood stabilizers for adolescents: A literature review].Encephale. 2017 Oct;43(5):464-470. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.09.005. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 27871720 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A Combination of Low Doses of Lithium and Valproate Improves Cognitive Outcomes after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2025 Mar;42(5-6):437-453. doi: 10.1089/neu.2024.0311. Epub 2024 Oct 28. J Neurotrauma. 2025. PMID: 39463282
References
-
- Katz IR, Rogers MP, Lew R, Thwin SS, Doros G, Ahearn E, et al. Lithium treatment in the prevention of repeat suicide-related outcomes in veterans with major depression or bipolar disorder: a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022;79:24–32. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.3170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lambrichts S, Detraux J, Vansteelandt K, Nordenskjöld A, Obbels J, Schrijvers D, et al. Does lithium prevent relapse following successful electroconvulsive therapy for major depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2021;143:294–306. doi: 10.1111/acps.13277. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuperberg M, Köhler-Forsberg O, Shannon AP, George N, Greenebaum S, Bowden CL, et al. Cardiometabolic risk markers during mood-stabilizing treatment: correlation with drug-specific effects, depressive symptoms and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2021;300:41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.12.047. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

