A population-based meta-analysis of circulating GFAP for cognition and dementia risk
- PMID: 36056631
- PMCID: PMC9539381
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51652
A population-based meta-analysis of circulating GFAP for cognition and dementia risk
Abstract
Objective: Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a marker of reactive astrocytosis, colocalizes with neuropathology in the brain. Blood levels of GFAP have been associated with cognitive decline and dementia status. However, further examinations at a population-based level are necessary to broaden generalizability to community settings.
Methods: Circulating GFAP levels were assayed using a Simoa HD-1 analyzer in 4338 adults without prevalent dementia from four longitudinal community-based cohort studies. The associations between GFAP levels with general cognition, total brain volume, and hippocampal volume were evaluated with separate linear regression models in each cohort with adjustment for age, sex, education, race, diabetes, systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medication, body mass index, apolipoprotein E ε4 status, site, and time between GFAP blood draw and the outcome. Associations with incident all-cause and Alzheimer's disease dementia were evaluated with adjusted Cox proportional hazard models. Meta-analysis was performed on the estimates derived from each cohort using random-effects models.
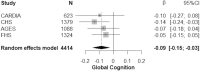
Results: Meta-analyses indicated that higher circulating GFAP associated with lower general cognition (ß = -0.09, [95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.15 to -0.03], p = 0.005), but not with total brain or hippocampal volume (p > 0.05). However, each standard deviation unit increase in log-transformed GFAP levels was significantly associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of incident all-cause dementia (Hazard Ratio [HR]: 2.47 (95% CI: 1.52-4.01)) and Alzheimer's disease dementia (HR: 2.54 [95% CI: 1.42-4.53]) over up to 15-years of follow-up.
Interpretation: Results support the potential role of circulating GFAP levels for aiding dementia risk prediction and improving clinical trial stratification in community settings.
© 2022 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Bryan is on the board of directors and owns stock in GalileoCDS, INC. Dr. Gonzales and her husband own stock in Abbvie. Dr Nasrallah has received honoria from Biogen and Eisai. Dr Pase has received honoria from Flordis. Dr Seshadri has received consulting fees from Biogen. Dr Yaffe is a board member of Alector. All other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01HC15103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG049607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 NS093634/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 NS100605/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 NS125513/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG20098/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG059421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 NS093634/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007412/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG059421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG15928/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG053325/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24AG065525/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS125513/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053325/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066524/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-25195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS017950;UF1NS125513/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG044271/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 AG071916/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92019D00031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG065525/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG066524/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
