The role of MRI-R2* in the detection of subclinical pancreatic iron loading among transfusion-dependent sickle cell disease patients and correlation with hepatic and cardiac iron loading
- PMID: 36057708
- PMCID: PMC9440968
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-022-01280-x
The role of MRI-R2* in the detection of subclinical pancreatic iron loading among transfusion-dependent sickle cell disease patients and correlation with hepatic and cardiac iron loading
Abstract
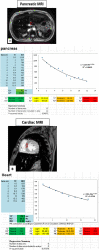
Objectives: Pancreatic reserve could be preserved by early assessment of pancreatic iron overload among transfusion-dependent sickle cell disease (SCD) patients. This study aimed to measure pancreatic iron load and correlate its value with patients' laboratory and radiological markers of iron overload.
Materials and methods: Sixty-six SCD children and young adults underwent MRI T2* relaxometry using a simple mathematical spreadsheet and laboratory assessment.
Results: The results indicated moderate-to-severe hepatic iron overload among 65.2% of studied cases. None had cardiac iron overload. Normal-to-mild iron overload was present in the pancreas in 86% of cases, and 50% had elevated serum ferritin > 2500 ug/L. There was no significant correlation between pancreatic R2* level, serum ferritin, and hepatic iron overload. Patients with higher levels of hemolysis markers and lower pre-transfusion hemoglobin levels showed moderate-to-severe pancreatic iron overload.
Conclusion: Chronically transfused patients with SCD have a high frequency of iron overload complications including pancreatic iron deposition, thereby necessitating proper monitoring of the body's overall iron balance as well as detection of extrahepatic iron depositions.
Keywords: MRI T2*; Pancreatic R2*; Sickle cell disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Agha M, Eid AF, Sallam M. Sickle cell anemia: imaging from head to toe. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 2013;44:547–561.
-
- Ware RE, Montalembert MD, Tshilolo L, Abboud MR. Sickle cell disease. Lancet. 2017;390:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Clark PR, St Pierre TG. Quantitative mapping of transverse relaxivity (1/T(2)) in hepatic iron overload: a single spin-echo imaging methodology. Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;18:431–438. - PubMed
-
- Fung EB, Harmatz P, Milet M, Ballas SK, De Castro L, Hagar W, Owen W, Olivieri N, Smith-Whitley K, Darbari D, Wang W, Vichinsky E, and the Multi-Center Study of Iron Overload Research Group Morbidity and mortality in chronically transfused Subjects with thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:255–265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

